Azides
Organic compounds that contain an azide functional group. Alkyl azides can be prepared by halide displacement, from alcohols via a variant of the Mitsunobu reaction with diphenyl phosphoryl azide, by ring-opening of epoxides and aziridines or by azidation of alkenes. Aryl azides can be prepared by displacement of the appropriate diazonium salt with sodium azide or with a sulfonamide first to a diazoamino sulfinate and then on hydrolysis the azide and a sulfinic acid (Dutt–Wormall reaction). Organic azides engage in useful organic reactions. They can be reduced to amines by hydrogenolysis or with a phosphines in the Staudinger reaction. They are also popular for their participation in the "click reaction" with alkynes to yield substituted 1,2,3-triazoles. Many of them are explosophores and poisons.
| Product name | Structure | CAS# | G-code | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2-Acetamido-3,4,6-tri-O-acetyl-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranosyl azide | 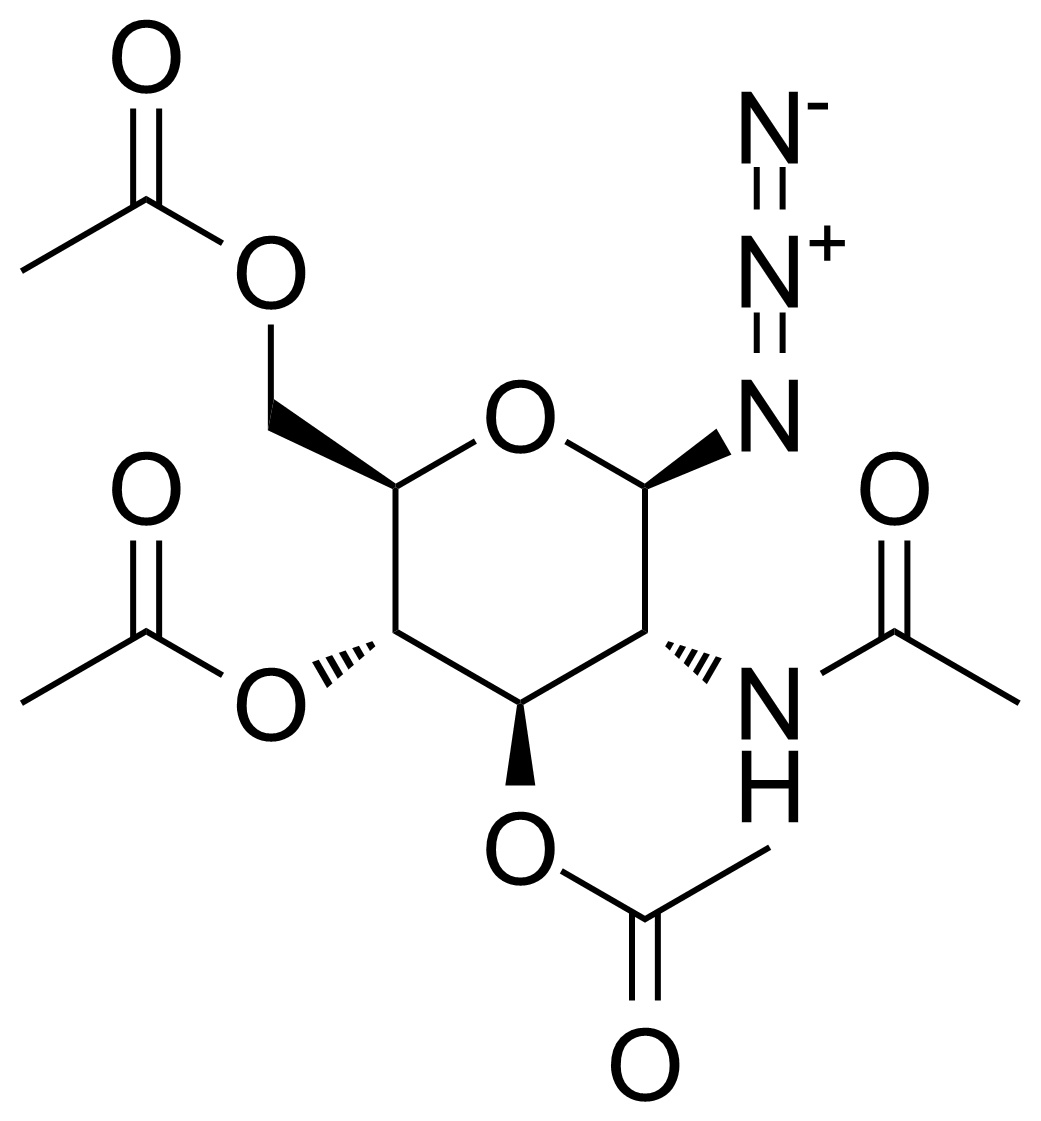 | [6205-69-2] | GEO-03200 | |
| 1-Azido-2-(trifluoromethyl)benzene | 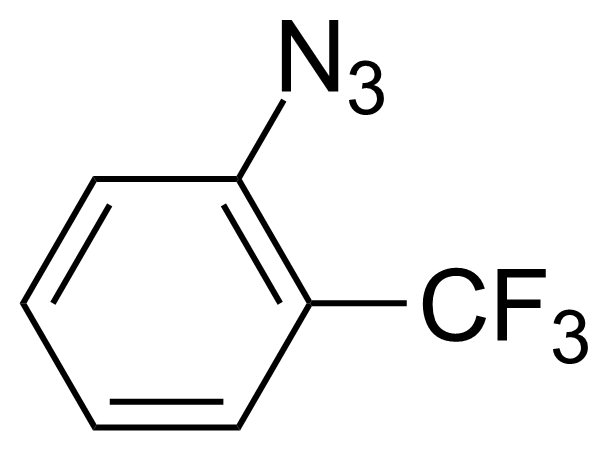 | [1548-68-1] | GEO-00244 | |
| 1-Azido-4-(trifluoromethyl)benzene | 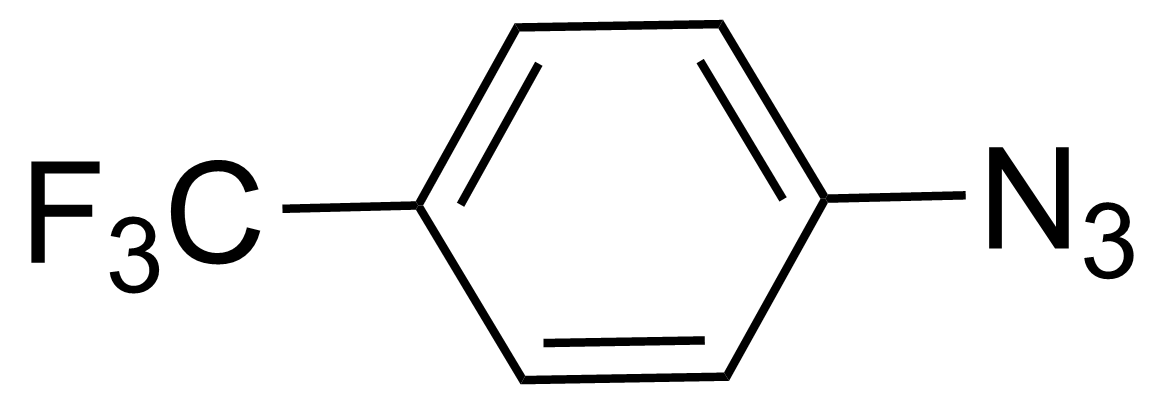 | [5586-13-0] | GEO-00245 |