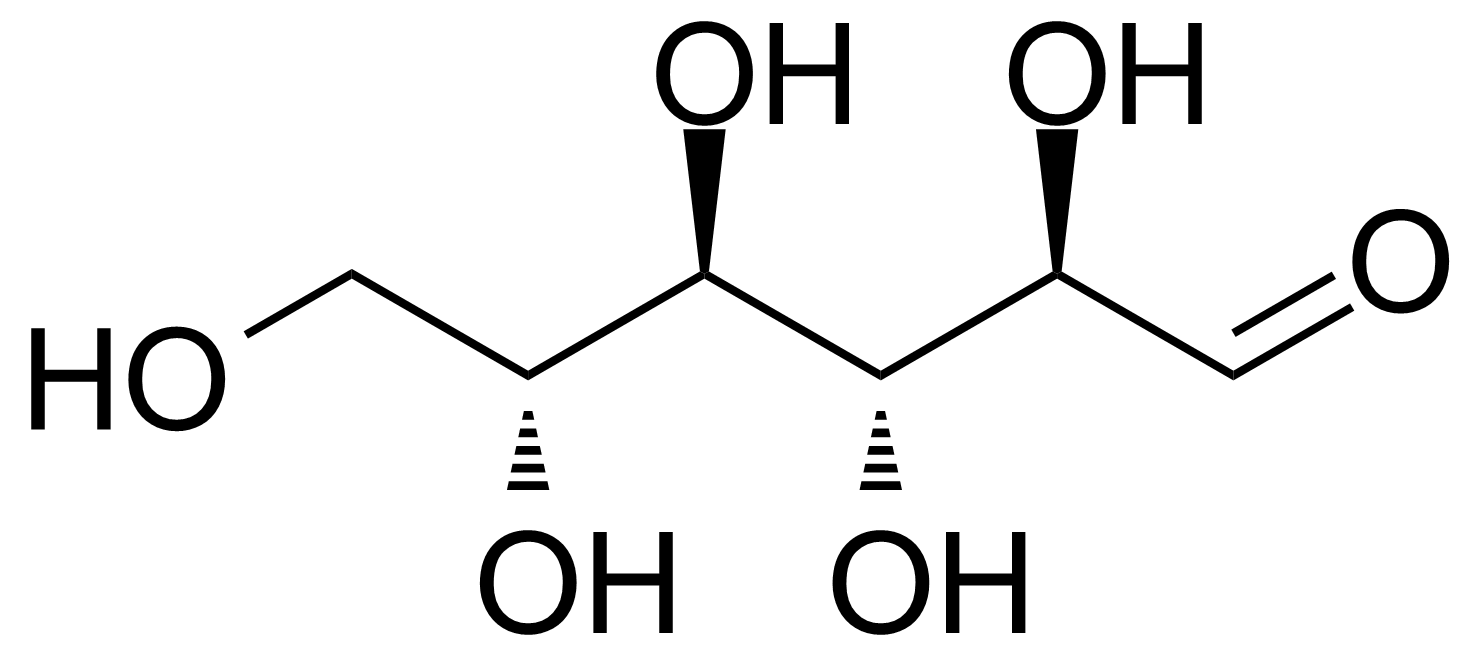
D-Allose
Produkt wurde eingestellt, aber wir haben Restbestände.
CAS-Nr.[2595-97-3]
G-CodeGEO-00057
EC-Nummer219-994-4
SummenformelC6H12O6
Molekulargewicht180,16
Synonyme
a/b-D-Allopyranose
Für weitere Informationen oder eine Anfrage senden Sie uns bitte eine E-Mail oder nutzen Sie unser Kontaktformular
Regulatorische Informationen
Dieses Produkt ist nicht klassifiziert.
Produktkategorisierung
Hauptkategorie
Zweite Ebene
Dritte Ebene
Beschreibung
D-Allose ist eine nützliche chemische Verbindung mit vielfältigen Forschungsanwendungen. Wir freuen uns, qualitativ hochwertige D-Allose in verschiedenen Größen (für Forschungs-, Pilotmaßstabs- oder Produktionsanwendungen) von Milligramm- bis Multi-Kilogramm-Chargen anbieten zu können, sodass Sie ganz einfach die richtige Menge für Ihre Bedürfnisse auswählen können.
Vollständige Beschreibung anzeigenUnfortunately, this article is currently only in English language. We are working on a translation. Thank you for understanding.
General description of D-Allose:
D-Allose (CPA) or β-D-Allopyranose [2595-97-3] is an aldohexose monosacharid, C-3 epimer of glucose. Pure comound is colorless (white) crystalline solid with the melting point of 141-142 °C[1] and a rotation at equilibrium [α] +14.5° in water.[2] It is classified as rare sugar. D-Allose is a low-calorie sweetener (20% less sweetness than sucrose), non-toxic and it can be easily dissolved in water but it is practically insoluble in methanol. It can be found in various plant species, such as Protea rubropilosa, Veronica filiformis, Mantzelia spp. Solanum tuberosum and others.[3] Convenient laboratory preparation is based on conversion of stereochemistry of C3-hydroxy group of 1,2,5,6-di-O-isopropylidene-α-D-glucofuranose by chemical oxidation to ketone and subsequent stereospecific reduction with borohydride followed by acetals hydrolysis with Amberlite H+ resine.[2] Large scale bioproduction strategy consists of enzymatic isomerisation of D-psicose (formed biochemically from D-fructose) to D-allose, catalysed by enzyme L-rhamonose isomerase.[4] Authors proposed the bioproduction strategy route to all rare sugars in a ring form as „Izumoring“.[5]Application:
Cancer and tumor inhibition is considered to be the most important property of D-allose. It has been reported to be effective against various human cancers.[6] Furthermore, radiation, when coupled with D-allose, stimulates the production of reactive oxygen species in cancer cells to a significantly higher extent and has an approximately five times larger effect on apoptosis.[7] It also acts as an immunosuppressant[8] and due to its anti-inflammatory effect, D-allose can also mitigate cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity.[9]Product categorization (Chemical groups):
Main category: Second level: Third level: ______________________________________________________________________________________[1] M. L. Wolfrom, J. N. Schumacher, H. S. Isabell, F. L. Humoller J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1954, 76, 5816.
[2] D.C. Baker, D. Horton, Ch. G. Tindall Jr. Carbohydr. Res. 1972, 24, 192.
[3] N. Mijailovic, A. Nesler, M. Perazzolli, E. A. Barka, A. Aziz Molecules 2021, 26, 1720.
[4] K. Morimoto, C. Park, M. Ozaki, K. Takeshita, T. Shimonishi, T. T. Granstrom, G. Takata, M. Tokuda, L. Izumori Enzyme Microb. Tech. 2006, 38, 855.
[5] T. B. Granstrom, G. Takata, M. Tokuda, K. Izumori J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2004, 97, 89.
[6] Z. Chen, J. Chen, W. Zhang, T. Zhang, C. Guang, W. Mu Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 426.
[7] H. Hoshikawa, K. Indo, T. Mori, N. Mori Cancer Lett. 2011, 306, 60.
[8] M.A. Hossain, H. Wakabayashi, F. Goda, S. Kobayashi, T. Maeba, H. Maeta Transplant. Proc. 2000, 32, 2021.
[9] Y. Iga, T. Matsuo J. Jpn. Soc. Nutr. Food Sci. 2010, 63, 17.
Ähnliche Produkte
| Produktname | Struktur | CAS-Nr. | G-Code | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1-Acenaphthenol | 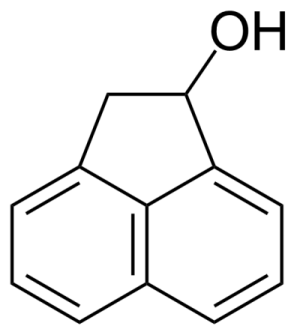 | [6306-07-6] | GEO-00001 | |
| 7-Acetamido-4-hydroxy-naphthalene-2-sulfonic acid | 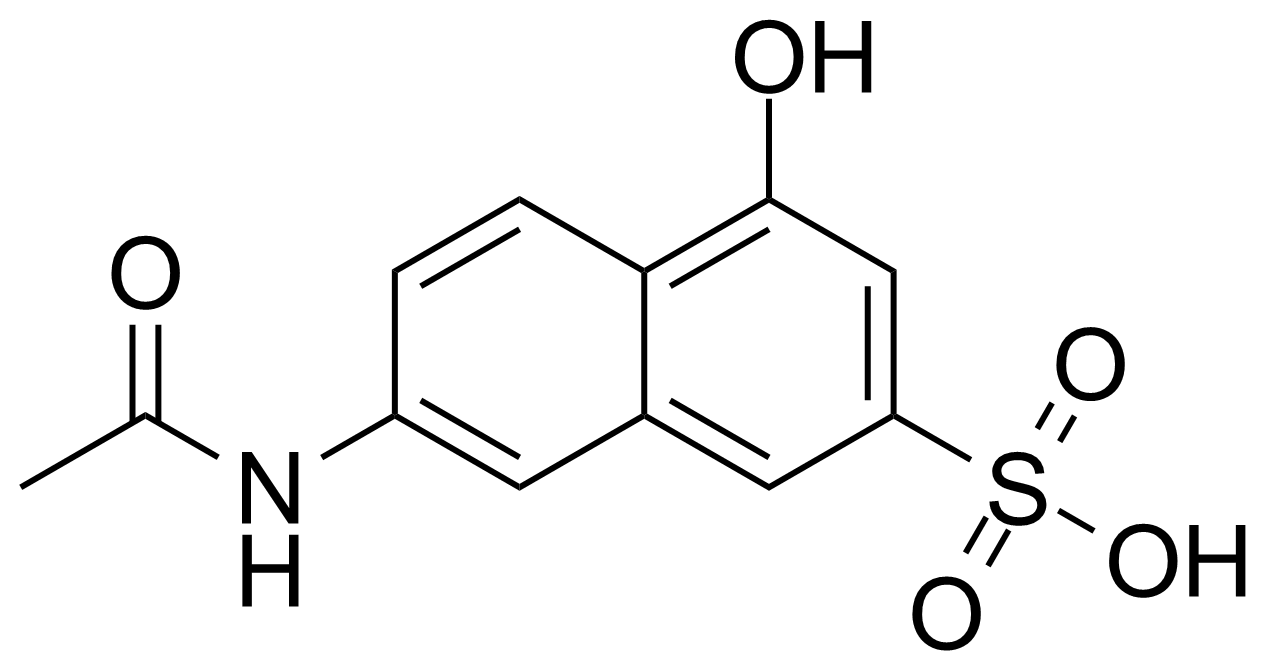 | [6334-97-0] | GEO-04013 | |
| 1-Adamantanemethanol | 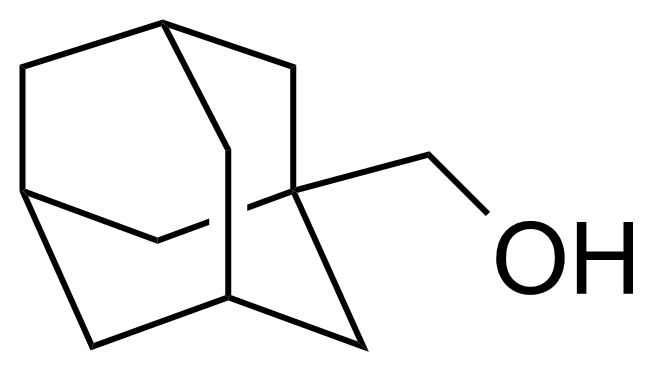 | [770-71-8] | GEO-04333 | |
| beta-D-Allopyranose | 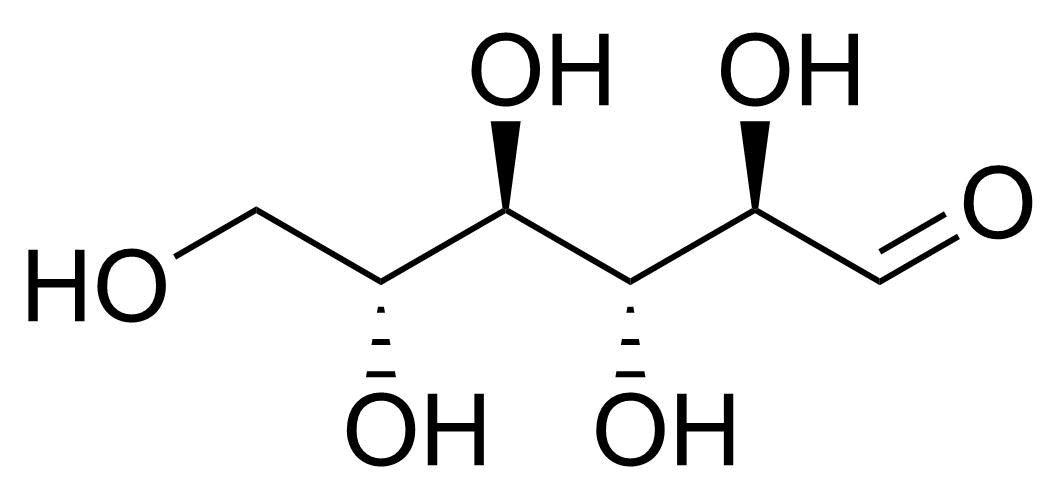 | [7283-09-2] | GEO-04660 | |
| D-Allose |  | [2595-97-3] | GEO-00057 | |
| L-Allose | 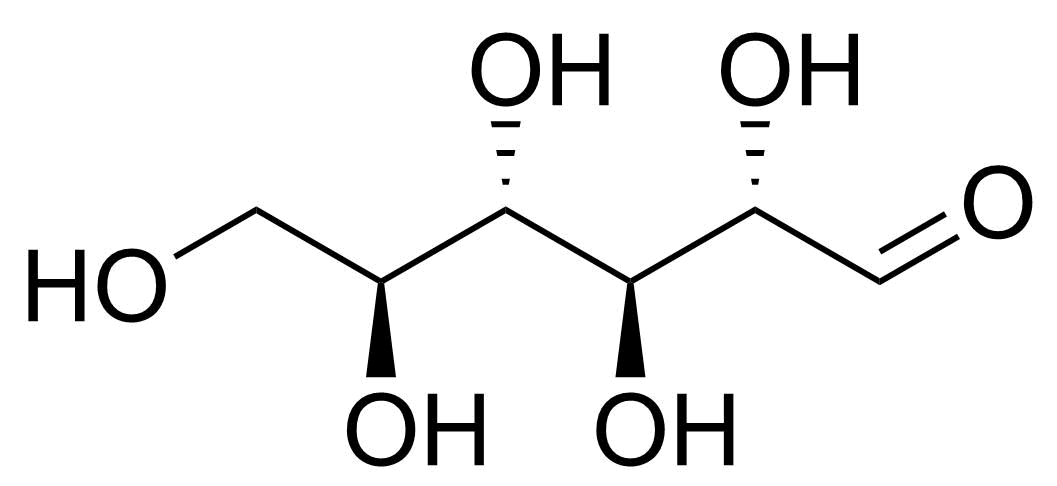 | [39392-62-6] | GEO-04661 | |
| 2-(Allyloxy)phenol | 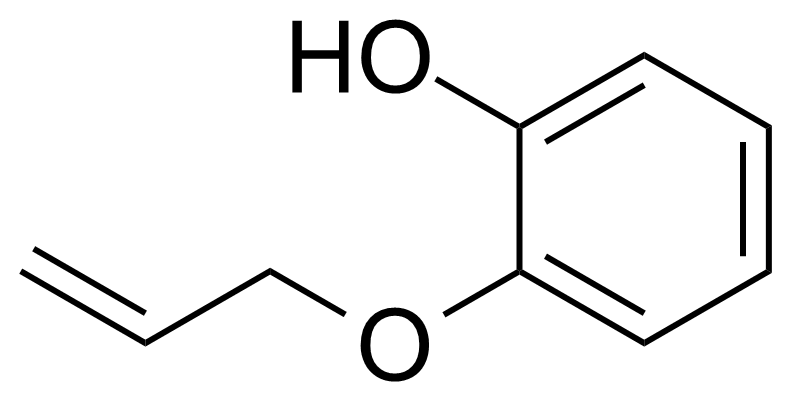 | [1126-20-1] | GEO-04471 | |
| D-Altrose | 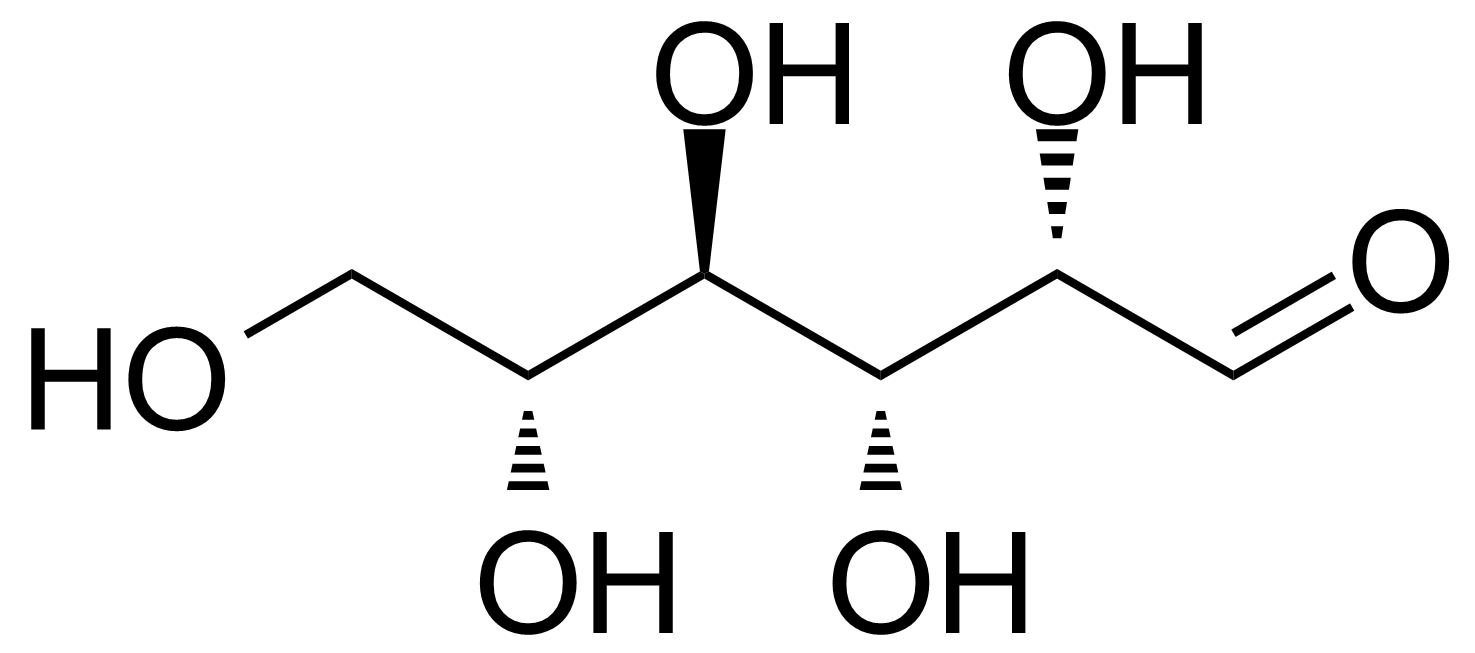 | [1990-29-0] | GEO-00058 | |
| L-Altrose | 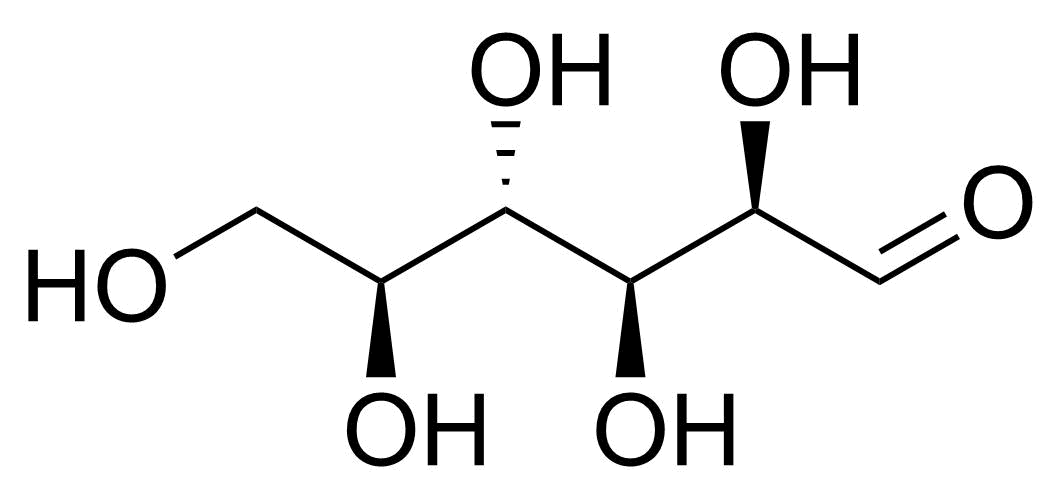 | [1949-88-8] | GEO-04662 | |
| (2R,4S)-2-Amino-4-cyclohexyl-4-hydroxybutanoic acid | 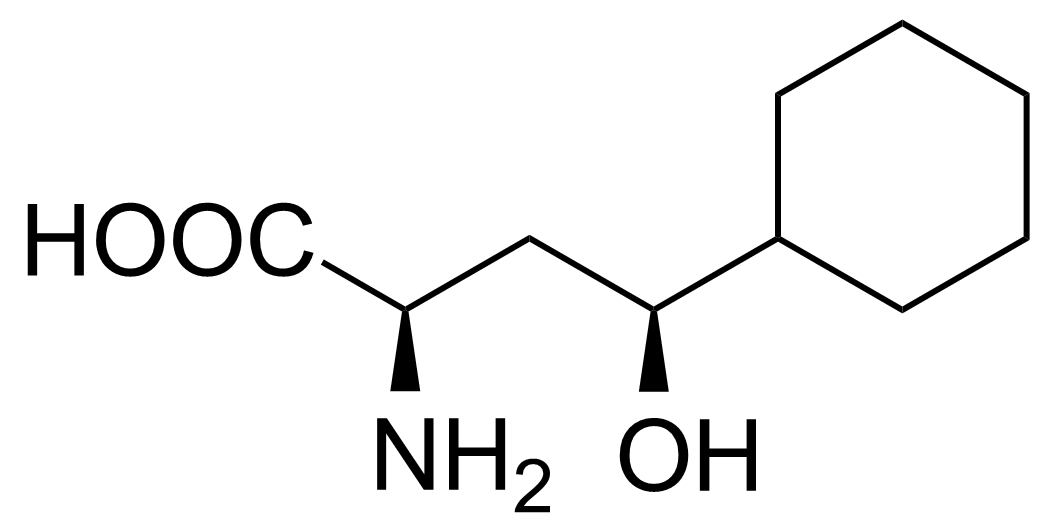 | [] | GEO-02717 |