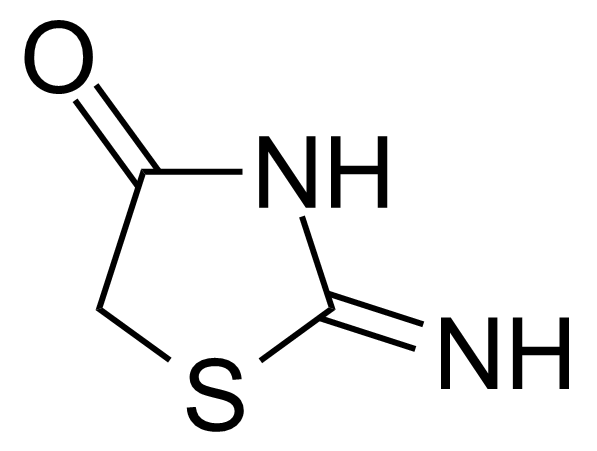
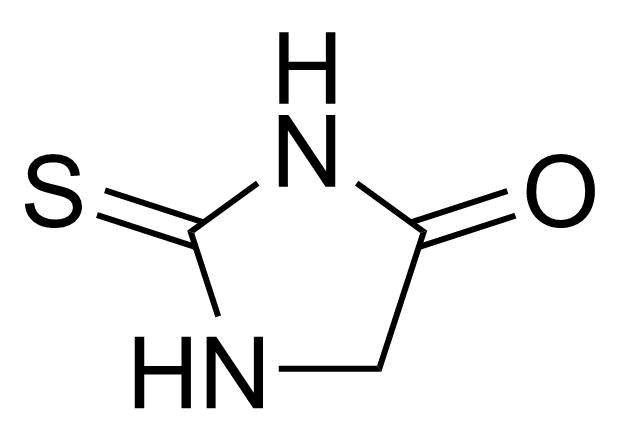
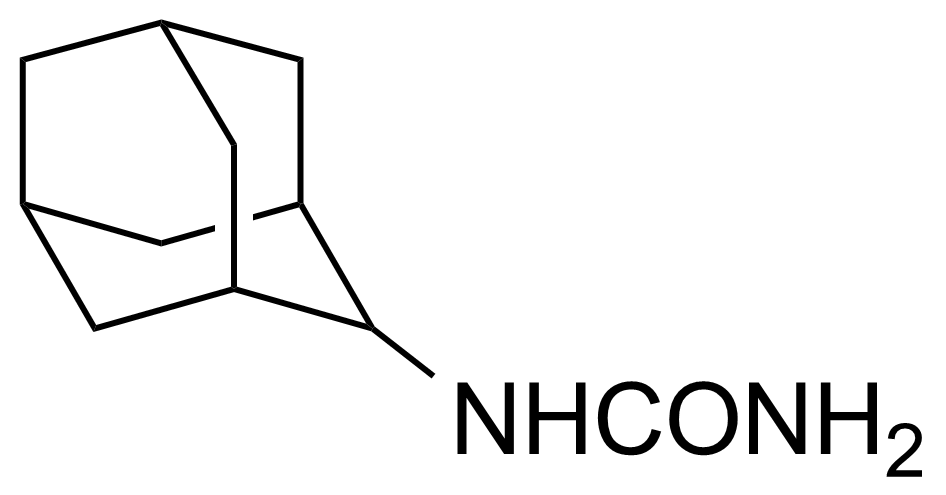
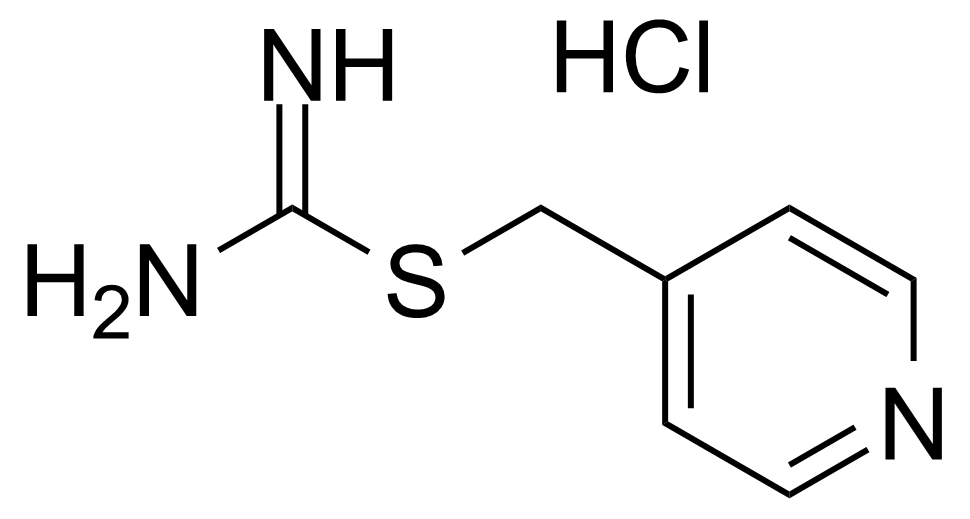
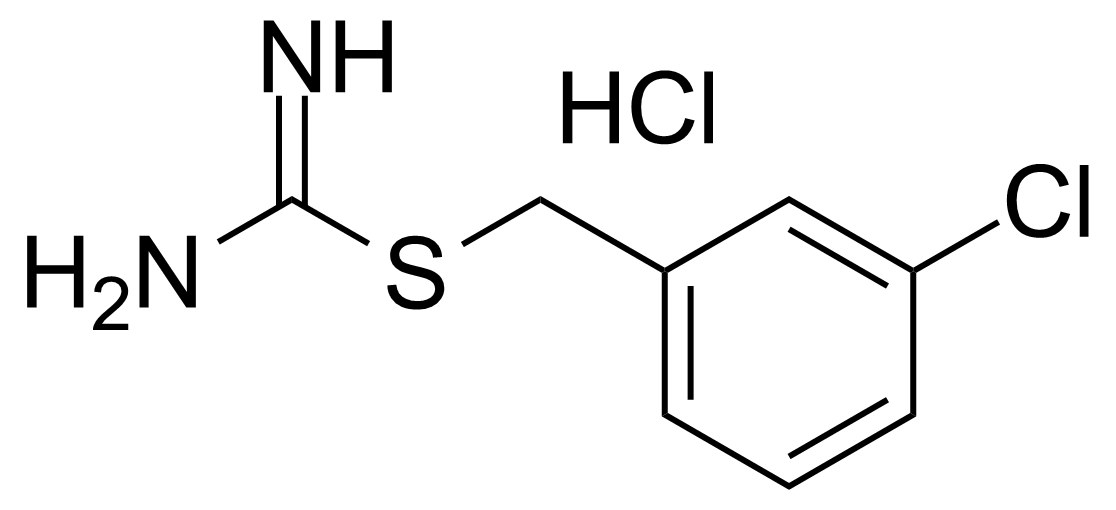
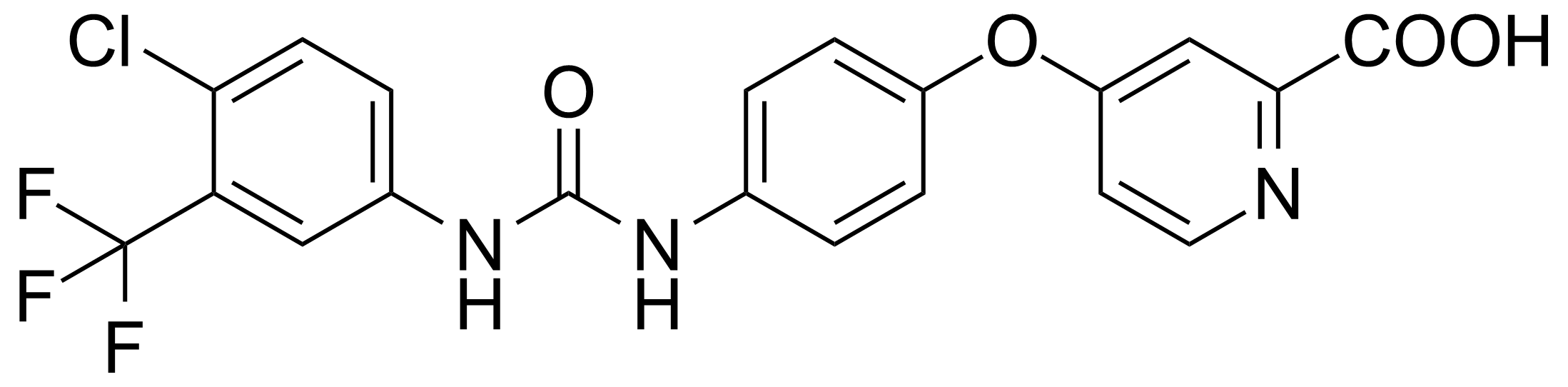
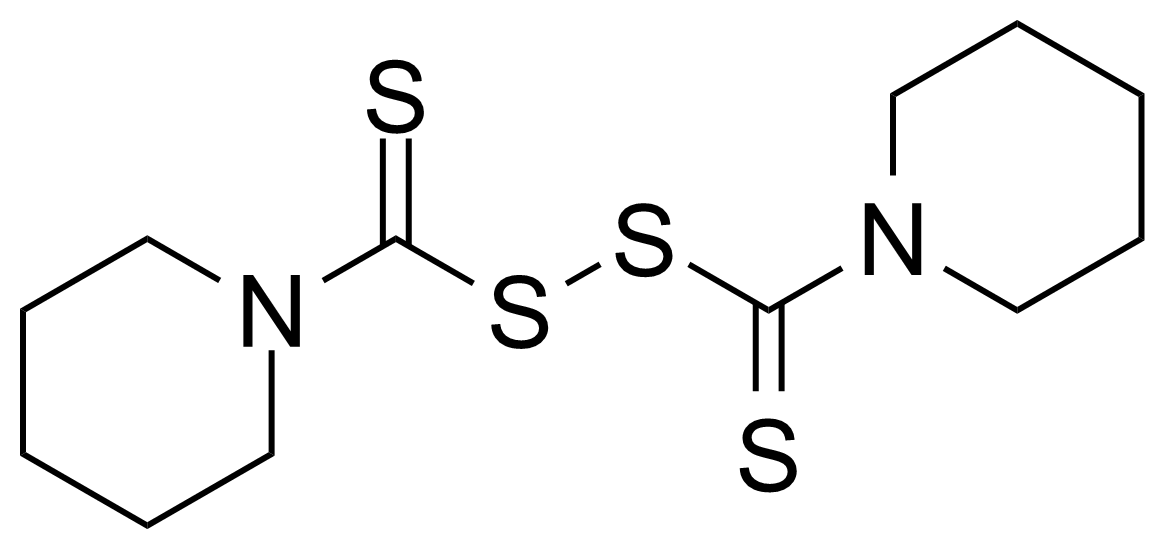
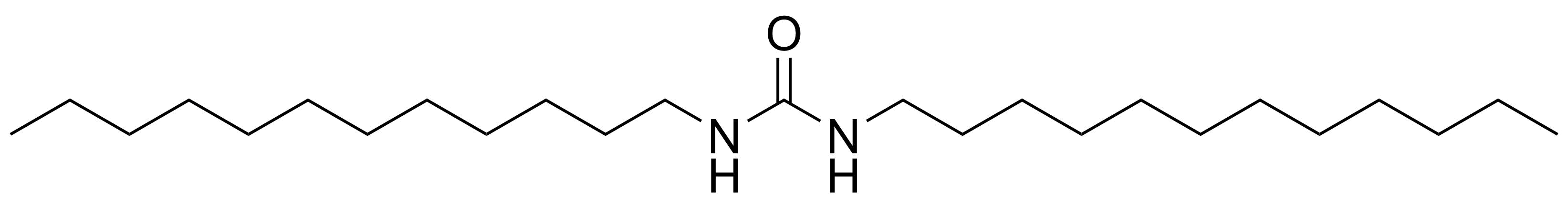
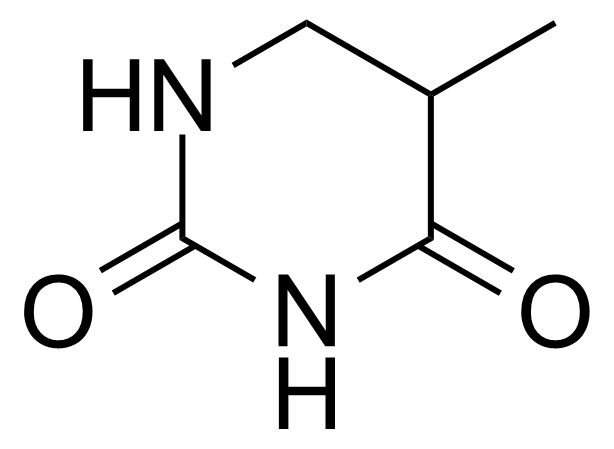
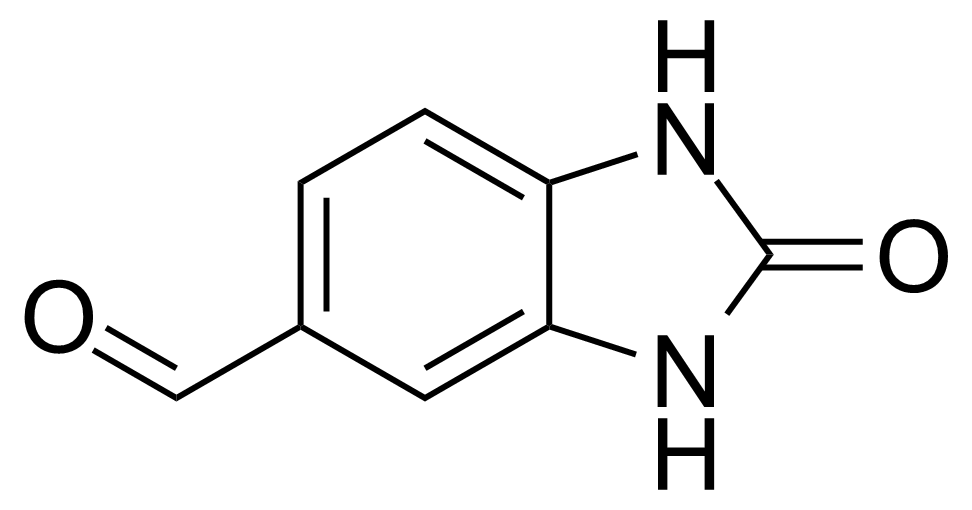
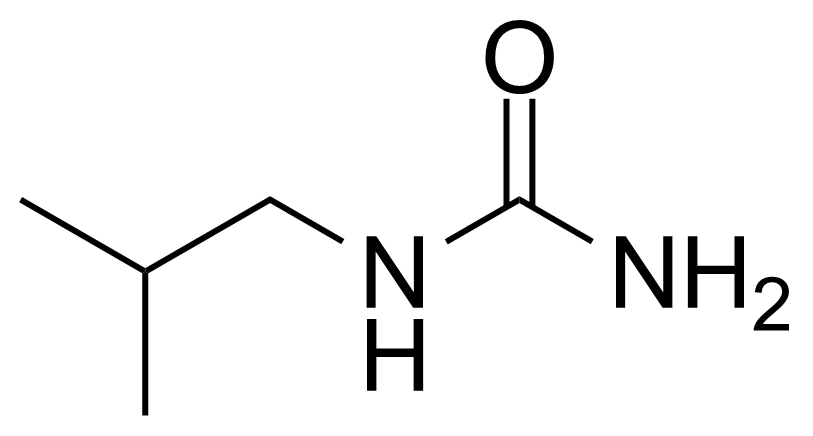
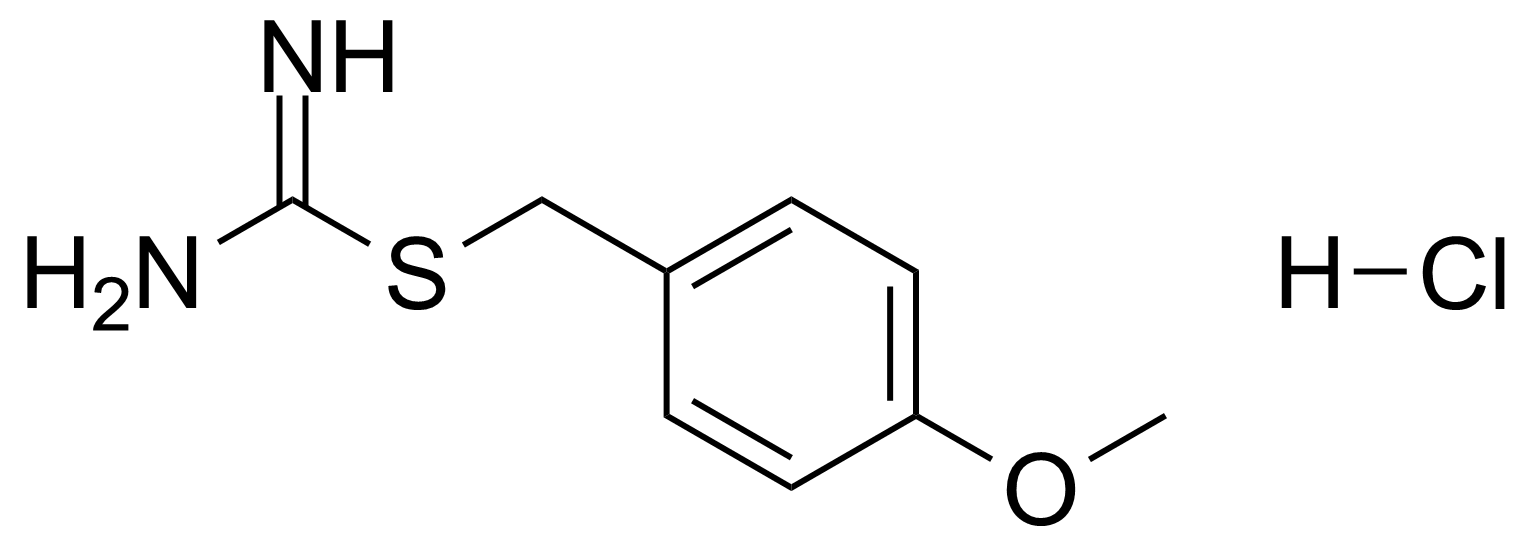
Urea / Thiourea derivatives / Guanidines
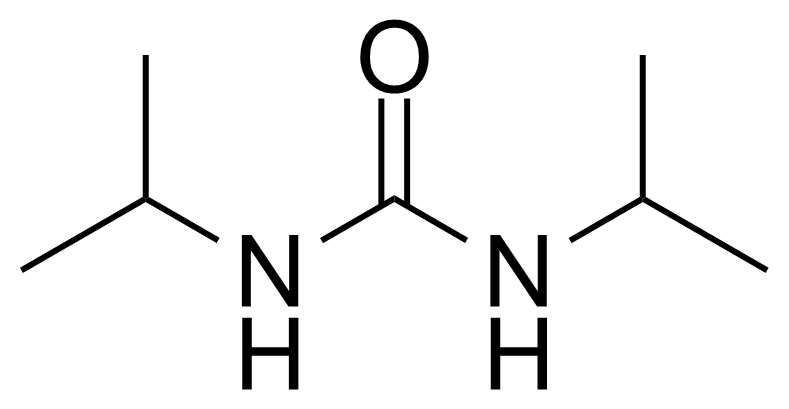
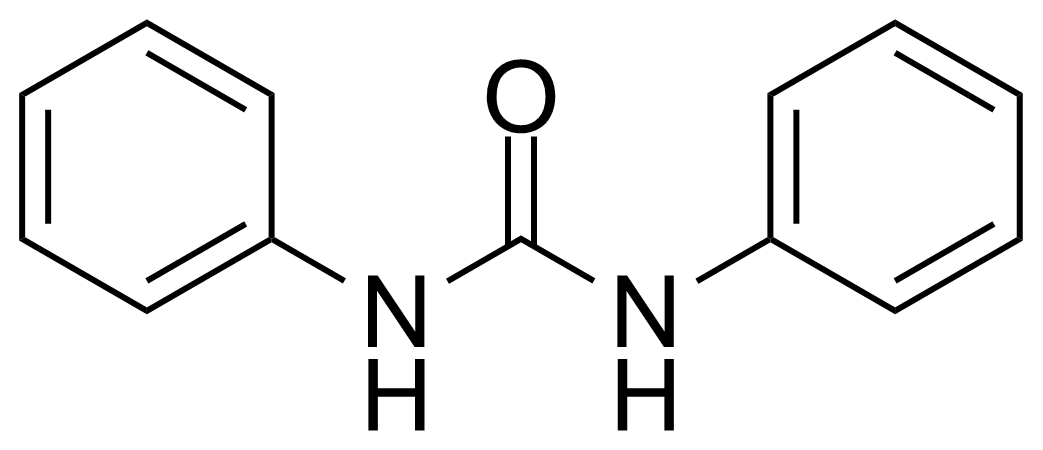
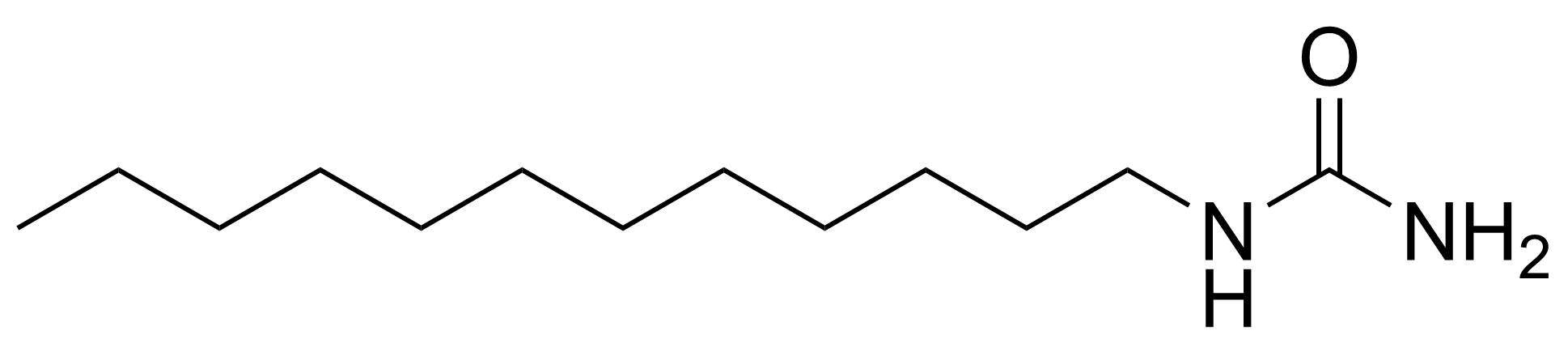
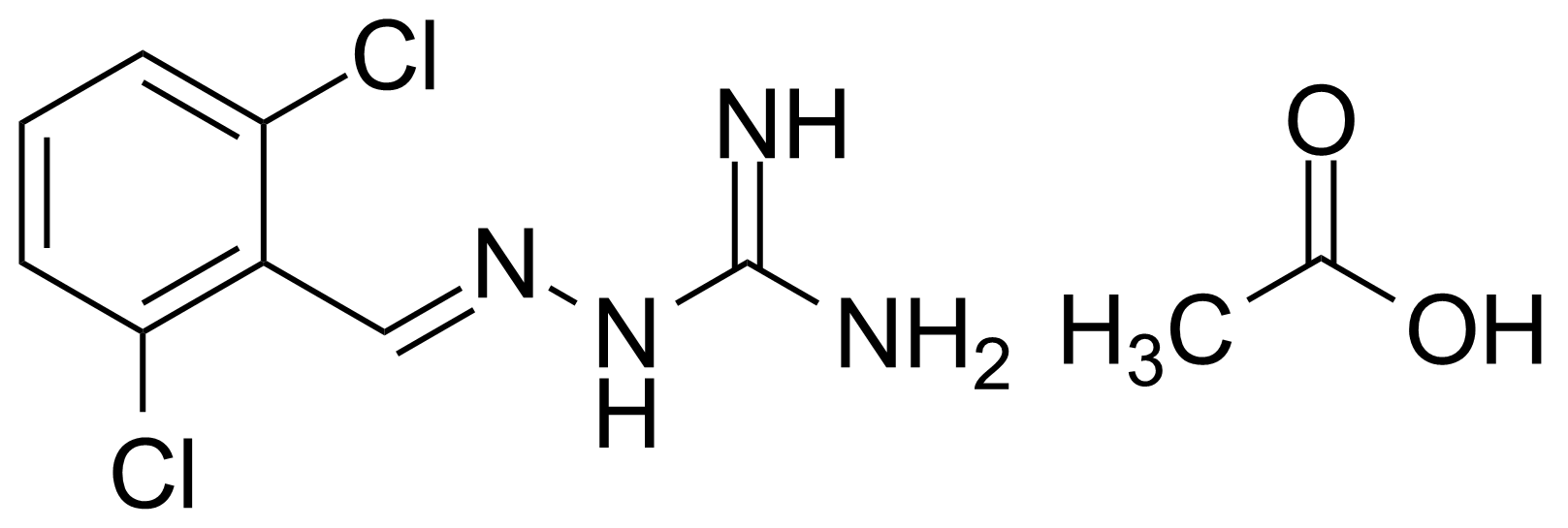
In chemistry, ureas are a class of organic compounds derived from urea (carbamide). Thioureas are sulfur analogues while guanidines are nitrogen analogues of ureas. Ureas can be prepared by transamidation of urea with alkyl and aryl amines, condensation of isocyanates with amines, condensation of ammonium salts and alkali metal cyanates. Ureas containing N-H bonds, including urea itself, are readily alkylated by aldehydes. Isobutylidene diurea (IBDU) is used as a slow-release fertilizer because in the soil it slowly hydrolyses, reverting to urea, an excellent source of fixed nitrogen. Analogously, thioureas can be prepared from thiourea by condensation with amines. Ureas and thioureas are green and sustainable catalysts for hydrogen-bond accepting substrates (carbonyls, imines, nitroalkenes etc.). Guanidine is a strong base that is used in the production of plastics and explosives. The main guanidine derivative of commercial interest is nitroguanidine (guanidinium nitrate) used as the gas generator in automobile airbags.
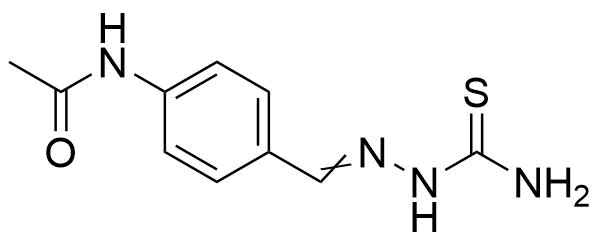
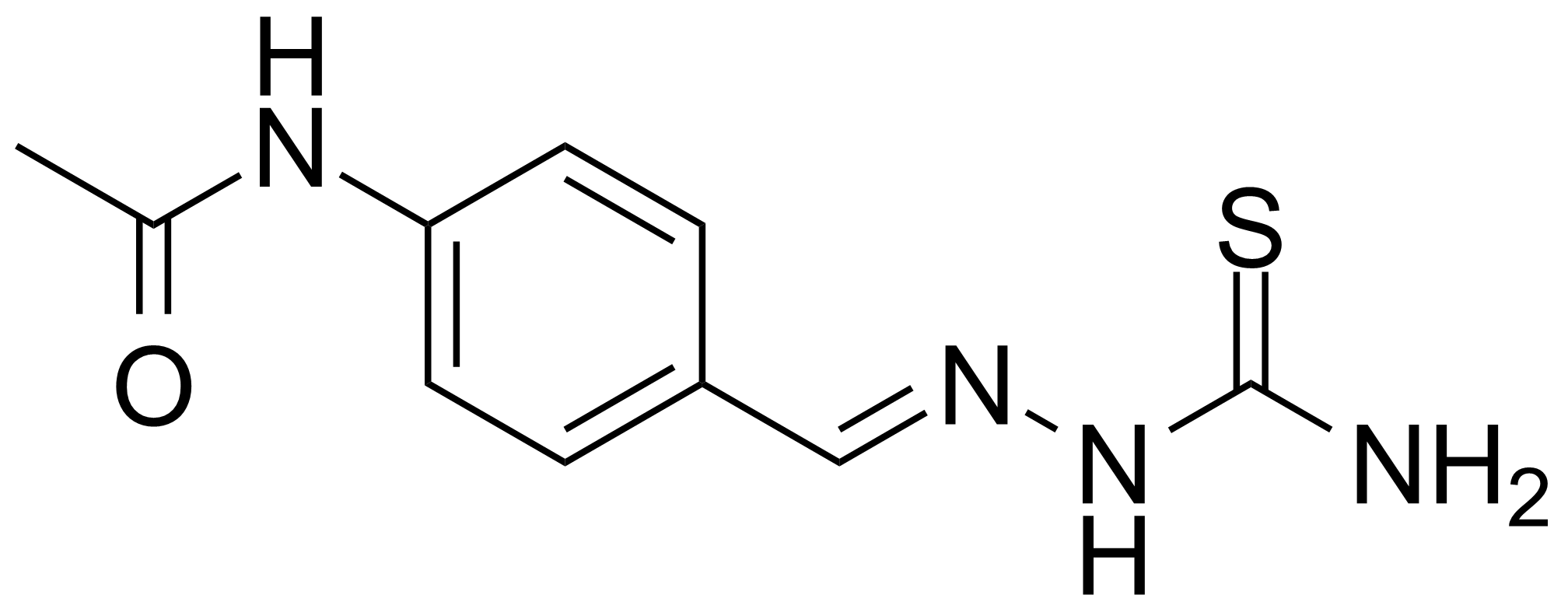

![Structure of Methyl 4-[(4-methoxycarbonylphenyl)carbamoylamino]benzoate](https://georganics.sk/wp-content/uploads/2021/05/GEO-04233_Methyl_4-4-methoxycarbonylphenylcarbamoylaminobenzoate.png)