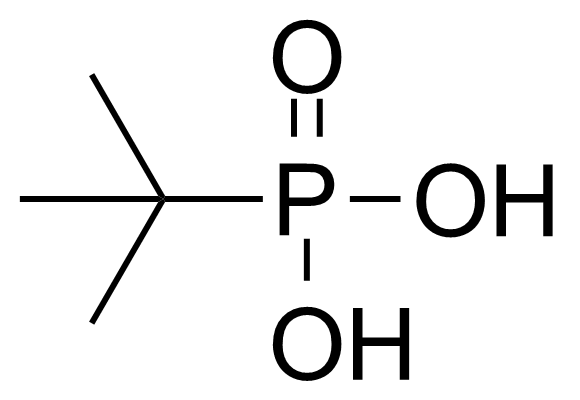
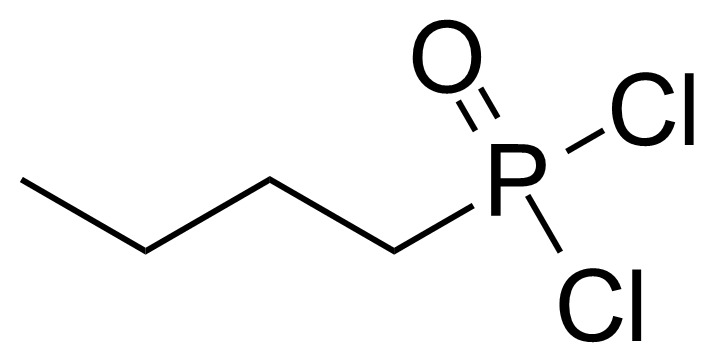
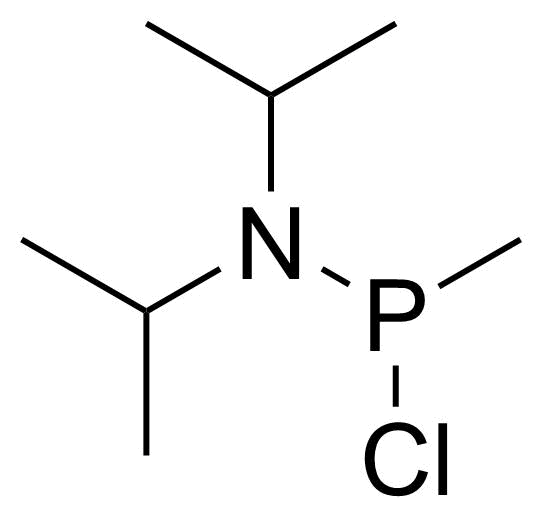
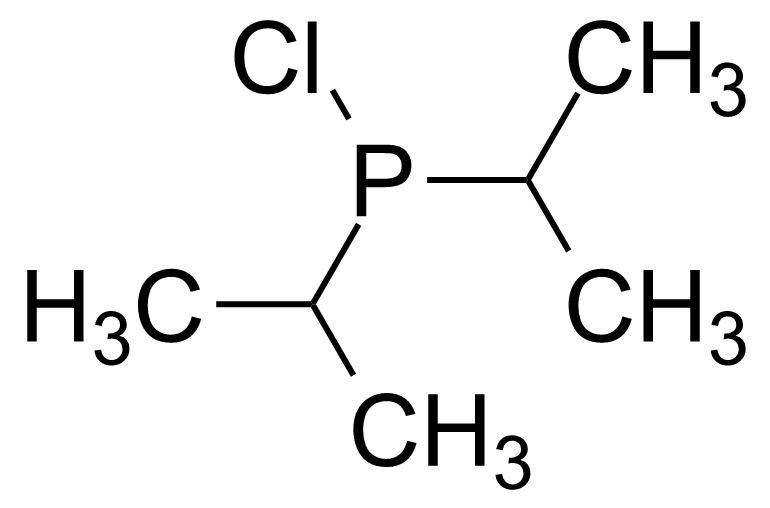
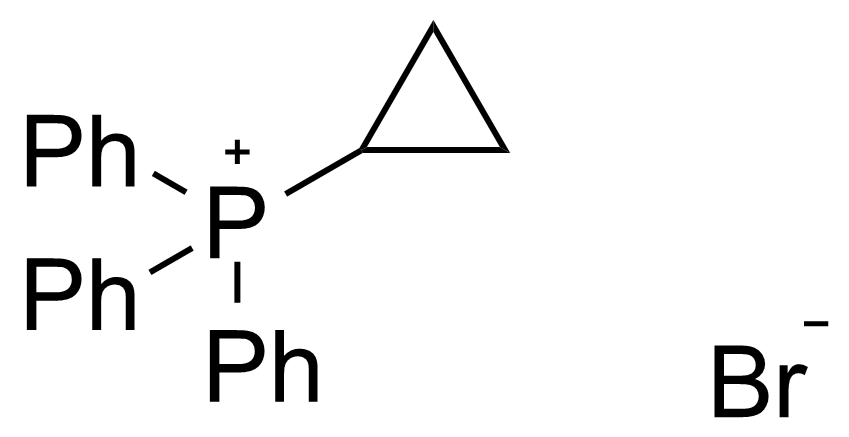Phosphorus reagents
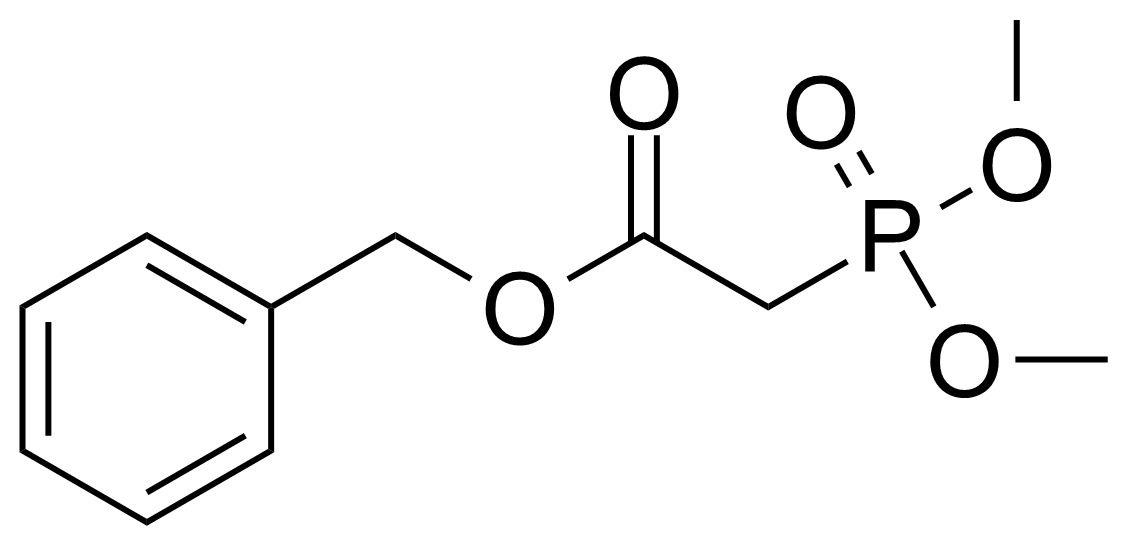
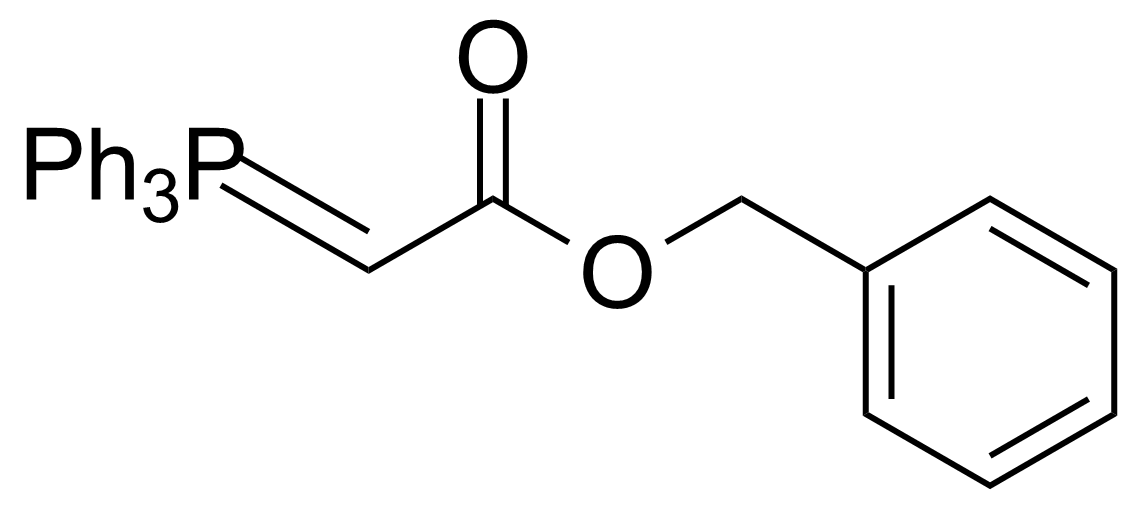
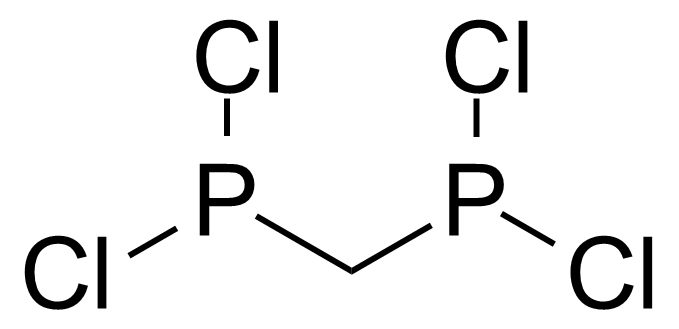
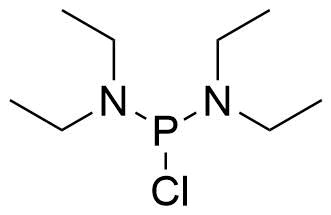
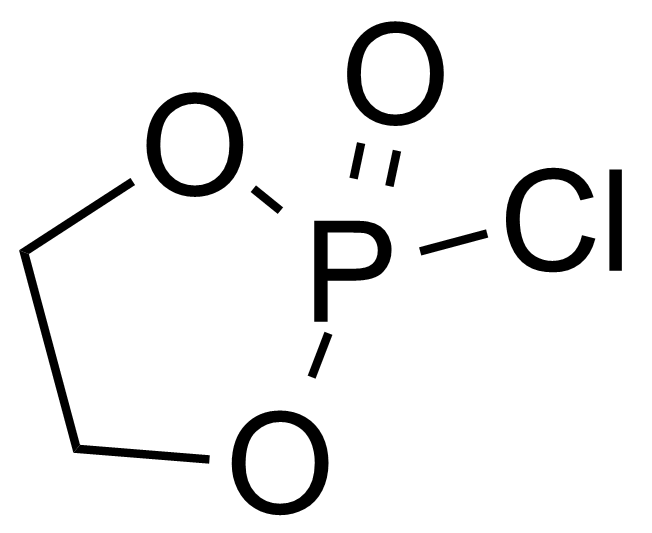
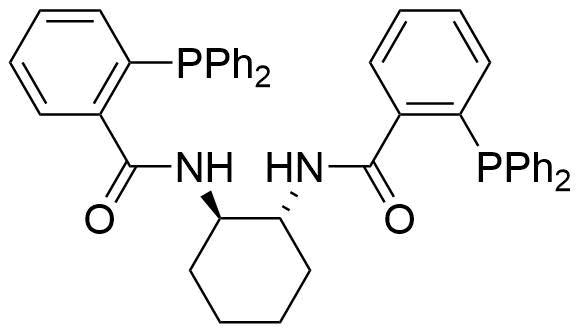
A class of compounds that contain P-C and P-O-C bonds are often classified as organophosphorus compounds. Phosphorus reagents are widely used commercially. Phosphorus can adopt a variety of oxidation states, and it is general to classify organophosphorus compounds based on their being derivatives of phosphorus(V) vs phosphorus (III), which are the predominant classes of compounds. Treatment of phosphorus trihalides with alcohols and phenols gives phosphites. Similar reactions occur for phosphorus oxychloride affording phosphates. Phosphonates are esters of phosphonic acid formed mainly by The Michaelis–Arbuzov reaction (trivalent phosphorus ester with an alkyl halide to form a pentavalent phosphorus species). Phosphonates are suitable reagents for Horner–Wadsworth–Emmons reaction or Seyferth-Gilbert homologation. Phosphorus ylides are unsaturated phosphoranes, widely used as Wittig reagents. Phosphines are nucleophilic catalysts in organic synthesis and reducing agents, as illustrated in the Staudinger reduction and in the Mitsunobu reaction for converting alcohols into esters. Organophosphorus compounds have many applications, including those in plasticisers, flame retardants, pesticides, extraction agents, nerve agents and water treatment.
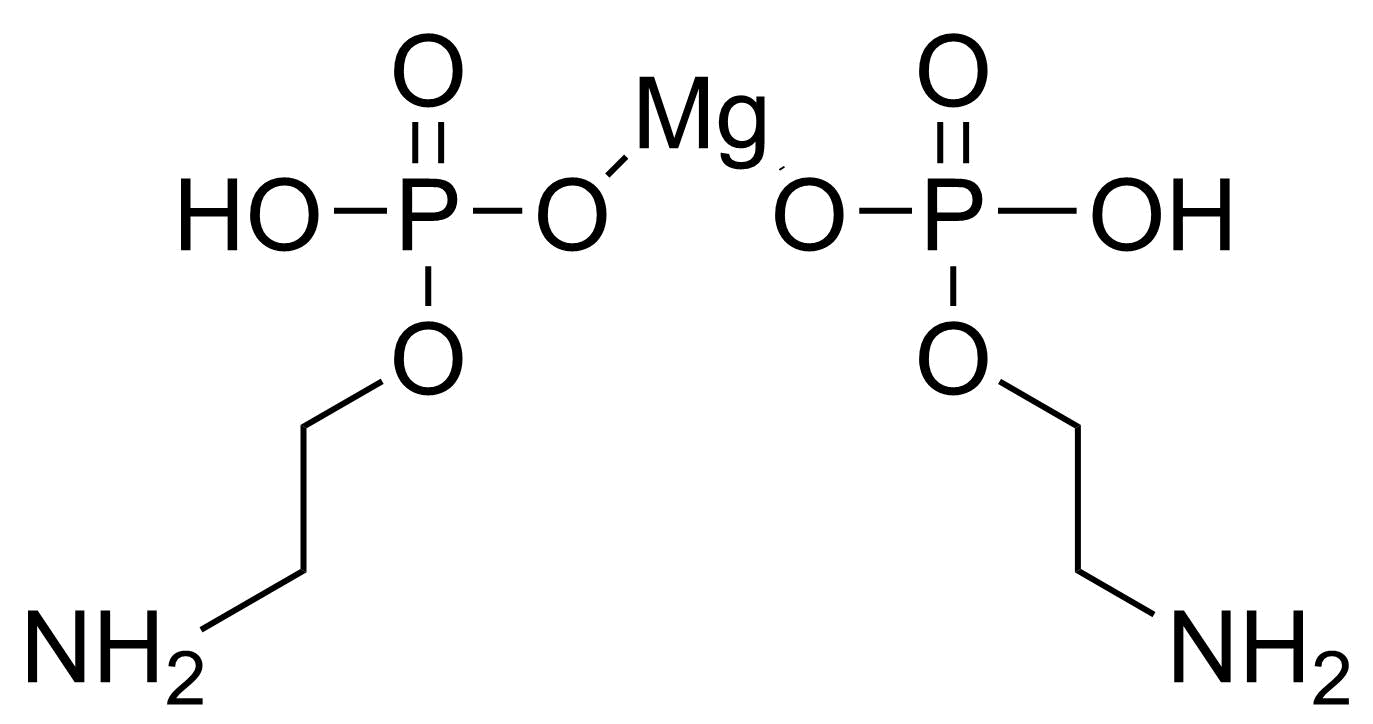
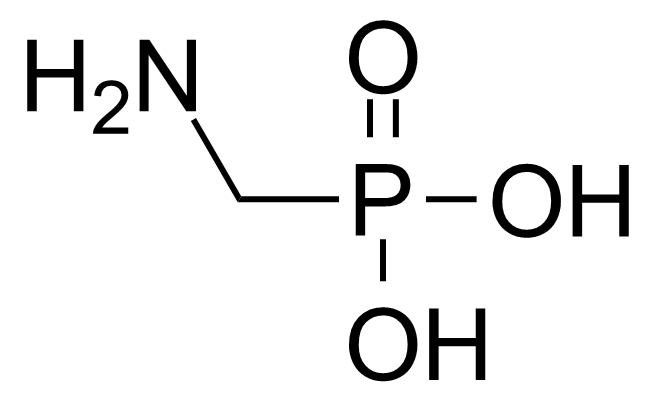
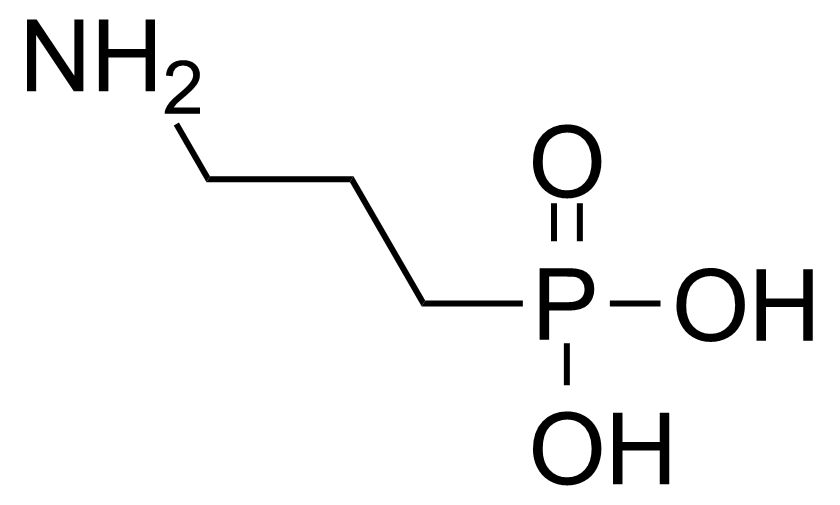
![Structure of Benzo[d]isoxazol-3-yl diphenyl phosphate](https://georganics.sk/wp-content/uploads/2021/05/GEO-00266_Benzodisoxazol-3-yl_diphenyl_phosphate.png)