N-Methyl-tert-butylamine
N-tert-Butylmethylamine

Für weitere Informationen oder eine Anfrage senden Sie uns bitte eine E-Mail oder nutzen Sie unser Kontaktformular
Regulatorische Informationen
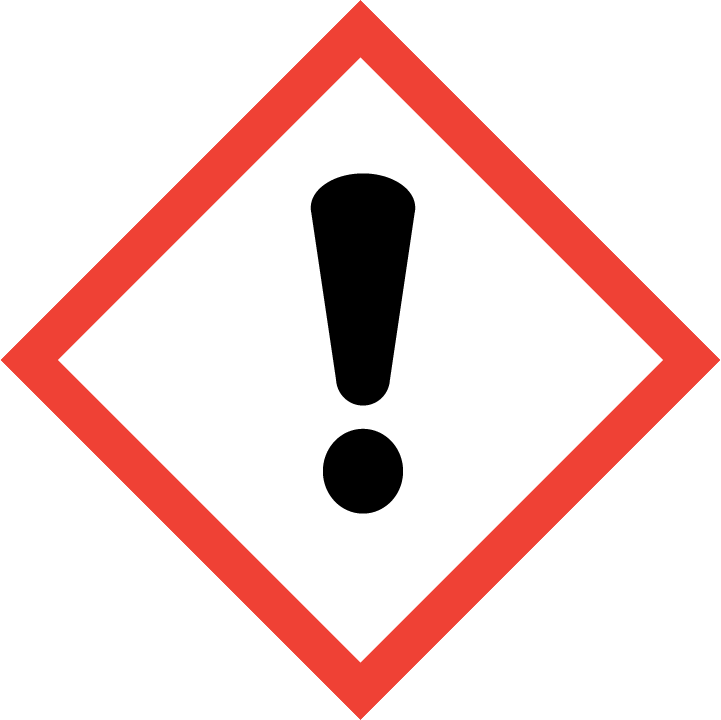
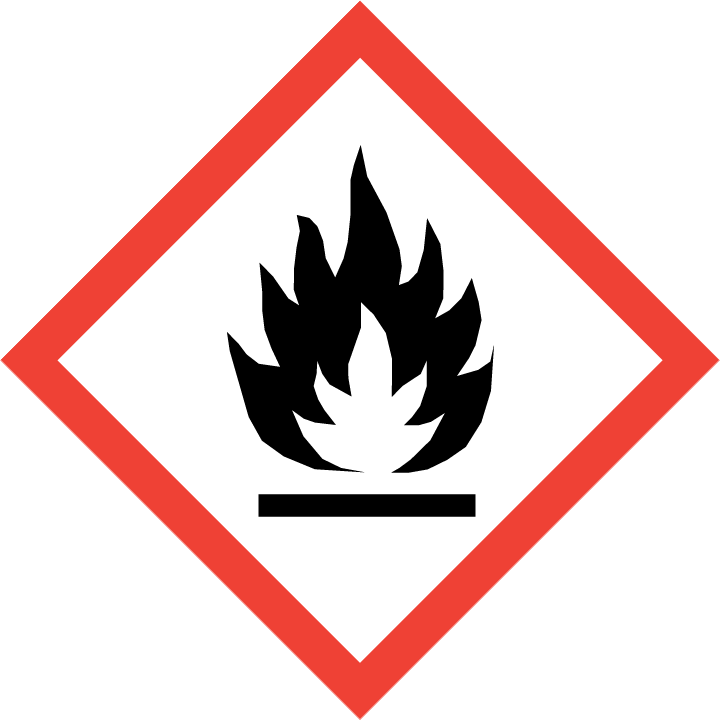

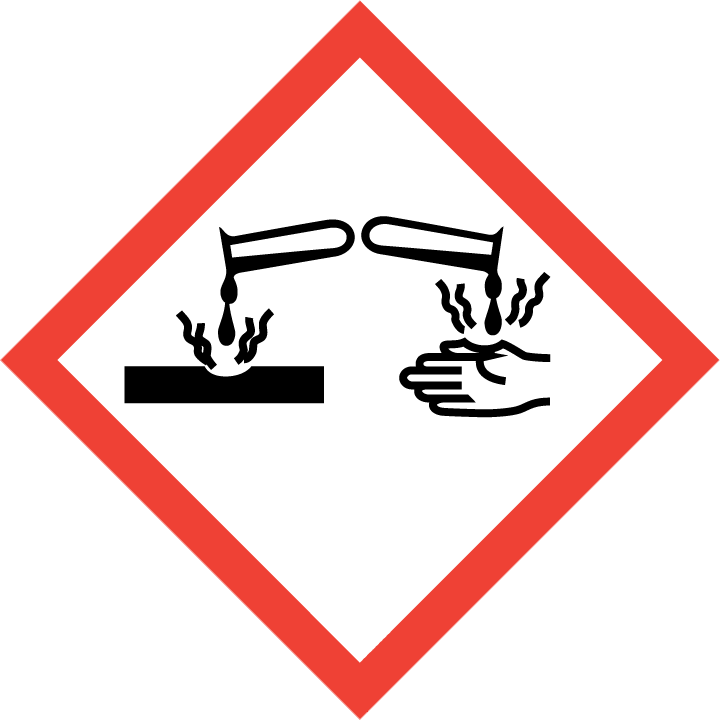

H225 – Flüssigkeit und Dampf leicht entzündbar.
H302+H312+H332 – Gesundheitsschädlich beim Verschlucken, Hautkontakt oder Einatmen.
H314 – Verursacht schwere Verätzungen der Haut und schwere Augenschäden.
P210 – Von Hitze/Funken/offener Flamme/heißen Oberflächen fernhalten. Nicht rauchen.
P233 – Behälter dicht verschlossen halten.
P240 – Behälter und zu befüllende Anlage erden.
P241 – Explosionsgeschützte elektrische Betriebsmittel/Lüftungsanlagen/Beleuchtung/… verwenden.
P242 – Nur funkenfreies Werkzeug verwenden.
P243 – Maßnahmen gegen elektrostatische Aufladungen treffen.
P261 – Einatmen von Staub/Rauch/Gas/Nebel/Dampf/Aerosol vermeiden.
P264 – Nach Gebrauch … gründlich waschen.
P270 – Bei Gebrauch nicht essen, trinken oder rauchen.
P271 – Nur im Freien oder in gut belüfteten Räumen verwenden.
P280 – Schutzhandschuhe/Schutzkleidung/Augenschutz/Gesichtsschutz tragen.
P301+P312+P330 – BEI VERSCHLUCKEN: Bei Unwohlsein GIFTINFORMATIONSZENTRUM/Arzt anrufen. Mund ausspülen.
P303+P361+P353 – BEI KONTAKT MIT DER HAUT (oder dem Haar): Alle beschmutzten, getränkten Kleidungsstücke sofort ausziehen. Haut mit Wasser abwaschen/duschen.
P304+P340+P310 – BEI EINATMEN: Die Person an die frische Luft bringen und für ungehinderte Atmung sorgen. Sofort GIFTINFORMATIONSZENTRUM/Arzt anrufen.
P305+P351+P338 – BEI KONTAKT MIT DEN AUGEN: Einige Minuten lang behutsam mit Wasser spülen. Vorhandene Kontaktlinsen nach Möglichkeit entfernen. Weiter spülen.
P362 – Kontaminierte Kleidung ausziehen und vor erneutem Tragen waschen.
P370+P378 – Bei Brand: … zum Löschen verwenden.
P403+P235 – Kühl an einem gut belüfteten Ort aufgewahren.
P405 – Unter Verschluss aufbewahren.
P501 – Inhalt/Behälter … zuführen.
Produktkategorisierung
Beschreibung
N-Methyl-tert-butylamine ist eine nützliche chemische Verbindung mit vielfältigen Forschungsanwendungen. Wir freuen uns, qualitativ hochwertige N-Methyl-tert-butylamine in verschiedenen Größen (für Forschungs-, Pilotmaßstabs- oder Produktionsanwendungen) von Milligramm- bis Multi-Kilogramm-Chargen anbieten zu können, sodass Sie ganz einfach die richtige Menge für Ihre Bedürfnisse auswählen können.
Vollständige Beschreibung anzeigenGeneral description and preparation:
N-Methyl-tert-butylamine [14610-37-8] (N-tert-Butylmethylamine or N-Methyl-2-methyl-2-propanamine) is a secondary amine and it is a colorless to pale yellow with the boiling point of 69 °C.[1] It is a highly flammable liquid and vapor. It is corrosive irritant that is harmful if inhaled, swallowed or in contact with skin. N-Methyl-tert-butylamine can be prepared by reductive N-methylation of tert-butylamine with carbon dioxide and diphenylsilane catalysed with caesium carbonate via initially formed t-butylformamide.[2] It can be also obtained from t-butylformamide by reduction with lithium aluminium tetrahydride or catalytic hydrogenation.[3]Application of N-Methyl-tert-butylamine:
N-Methyl-tert-butylamine as a secondary amine can undergo chemical reactions to form desired amines[4] and amides[5]. It was used in a SAR study related to N,N-disubstitutions of the terminal acetamide on pyrazolopyrimidines.[6] It was used in a new approach to pyrrolo[3,4-b]indole ring system via tri-n-butyltin hydride induced 1,5-radical translocation and 5-endo-trig cyclization of carboxamide formed from 3-trifluoroacetylindole and N-methyl-tert-butylamine.[7]Product categorization (Chemical groups):
Main category: Second level: _______________________________________________________________________Ähnliche Produkte
| Produktname | Struktur | CAS-Nr. | G-Code | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Neu | 5-Acetyl-2-amino-4-(2-furanyl)-6-methyl-4H-pyran-3-carbonitrile | 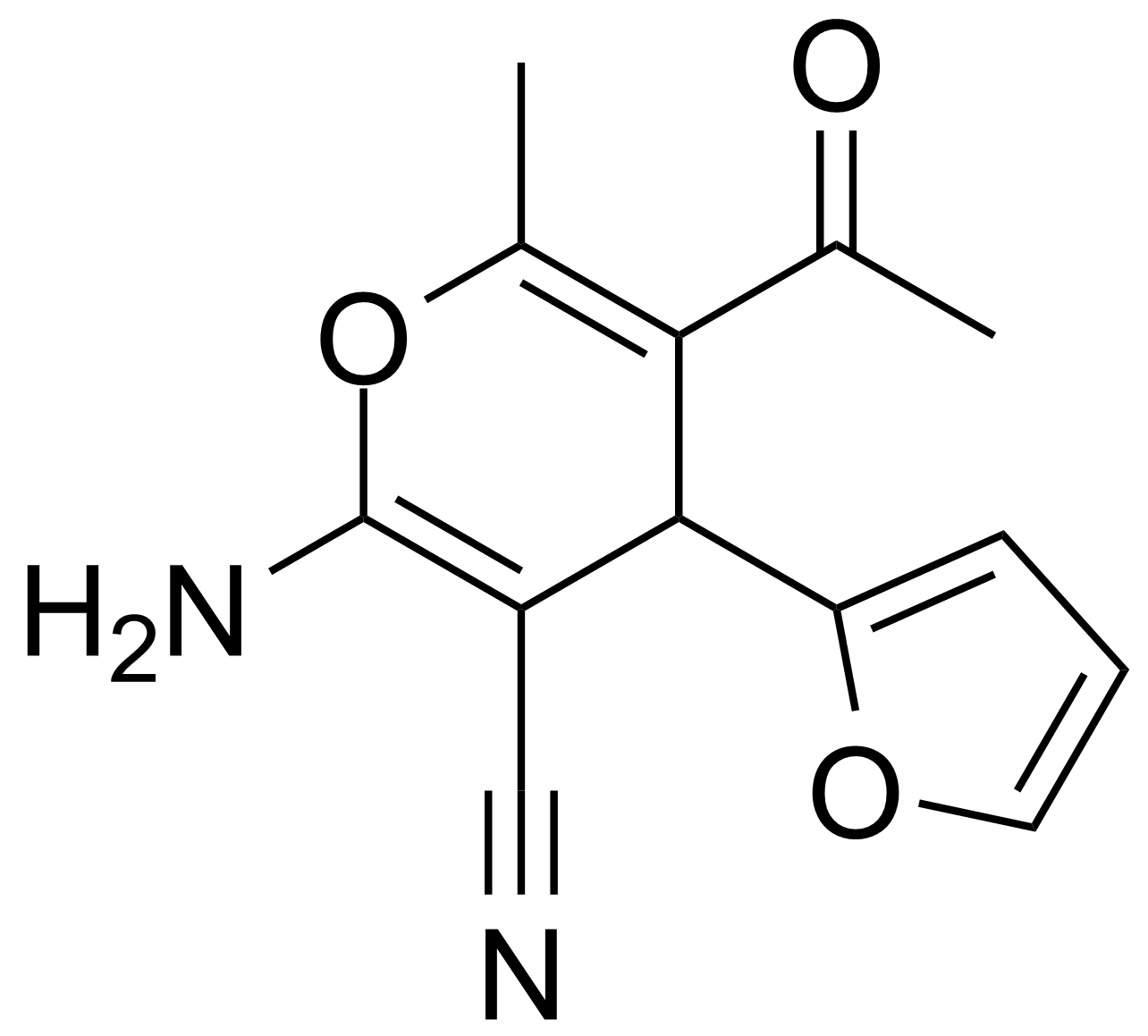 | [105263-08-9] | GEO-00016 |
| Neu | 5-Acetyl-2-amino-4-(4-methoxyphenyl)-6-methyl-4H-pyran-3-carbonitrile | 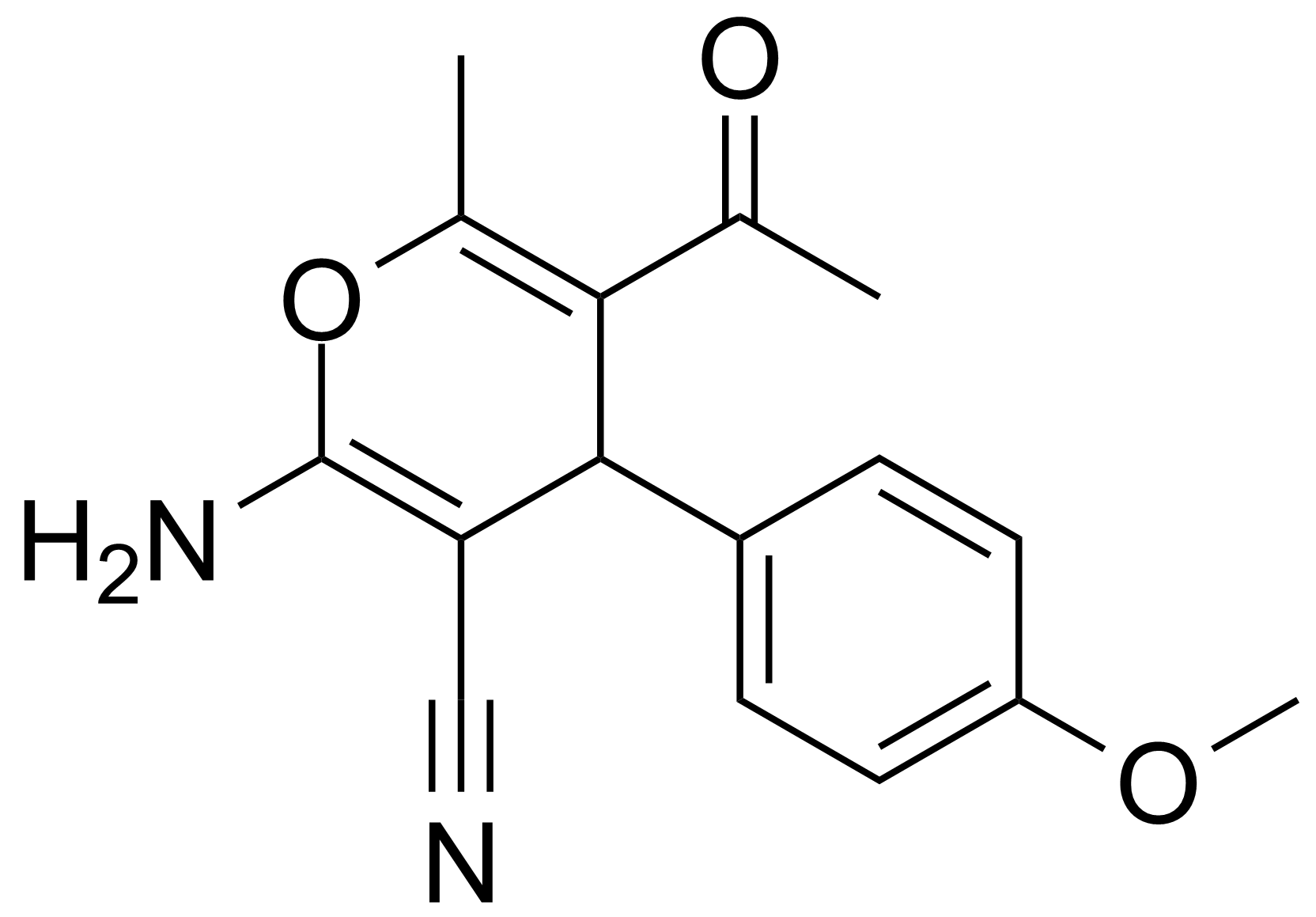 | [105263-07-8] | GEO-00017 |
| 5-Acetyl-2-amino-6-methyl-4-phenyl-4H-pyran-3-carbonitrile | 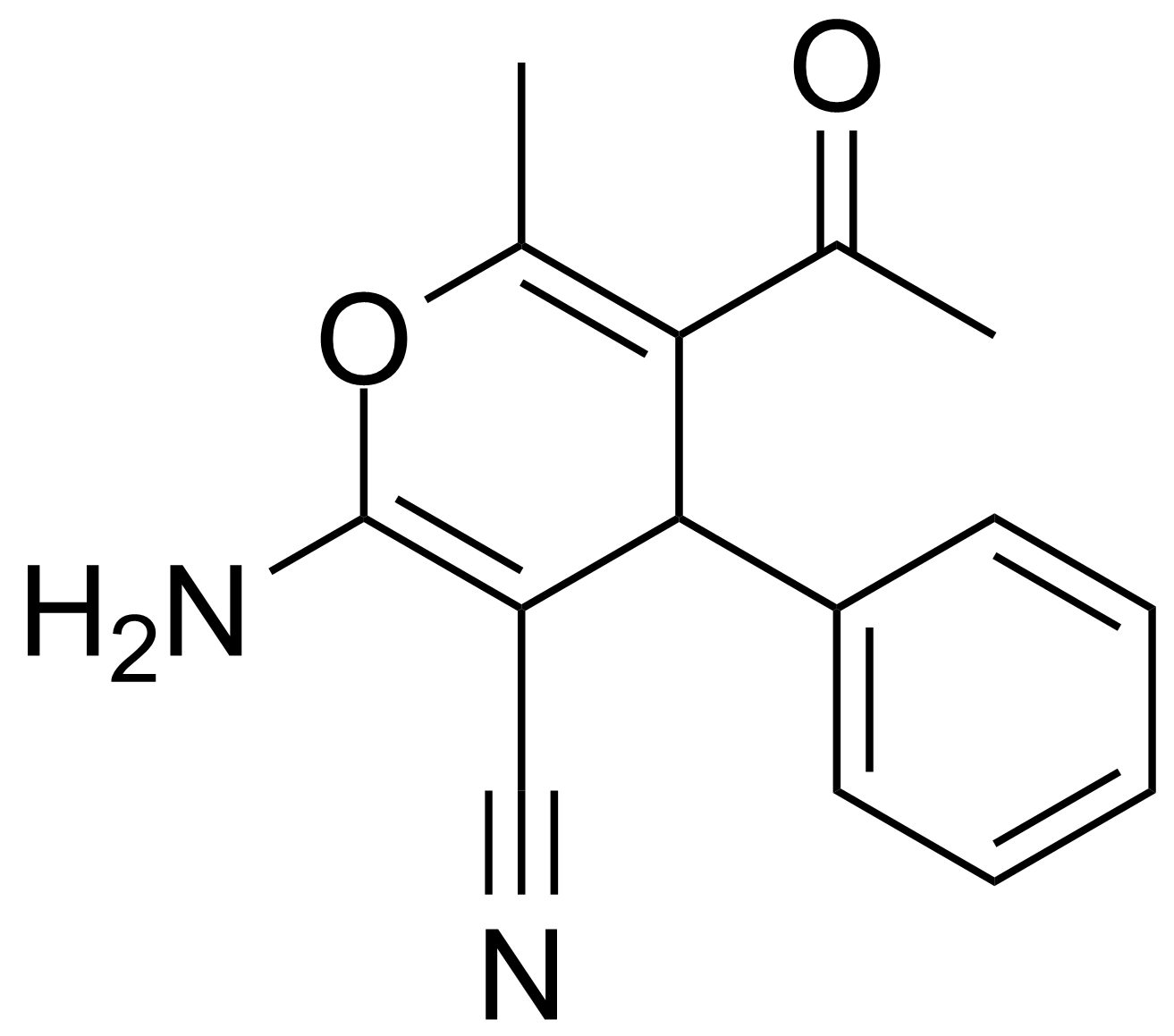 | [89809-89-2] | GEO-00018 | |
| Neu | 2-Acetylaminothiazole | 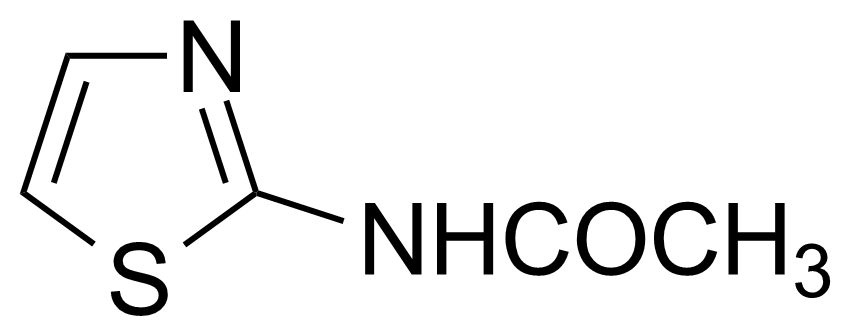 | [2719-23-5] | GEO-00020 |
| Neu | Allylcyclohexylamine | 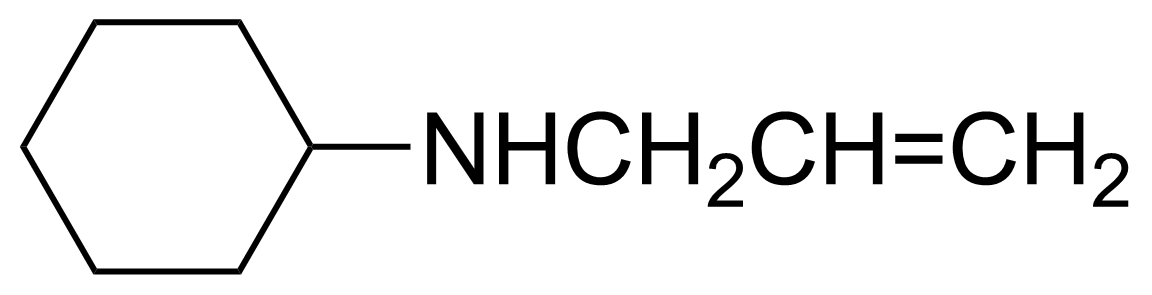 | [6628-00-8] | GEO-00059 |
| Neu | 4-Amino-2,1,3-benzothiadiazole | 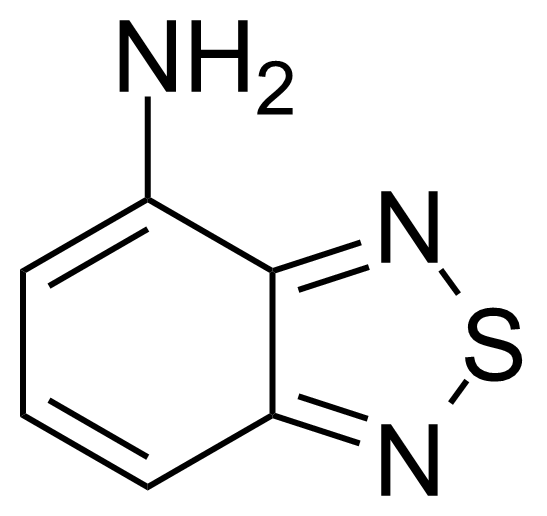 | [767-64-6] | GEO-00070 |
| Neu | 2-Aminobenzothiazole | 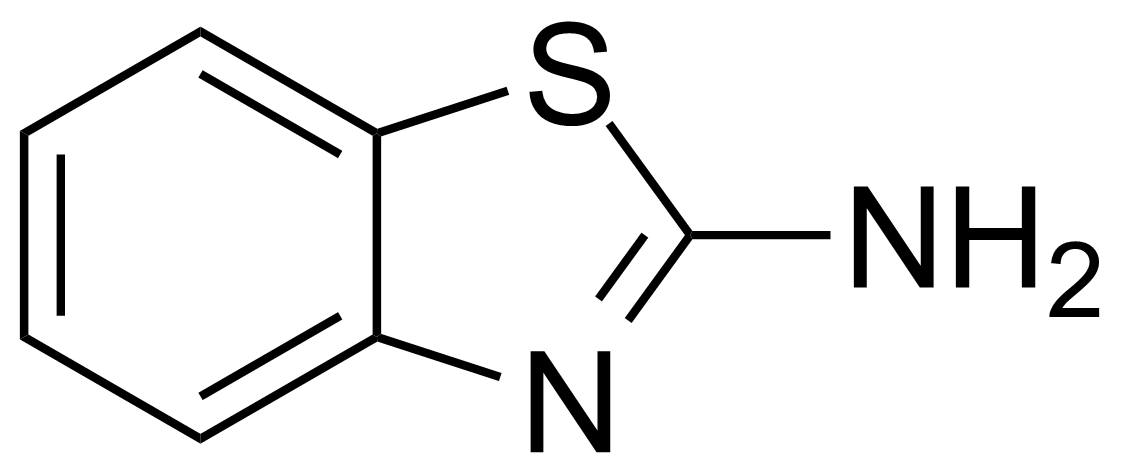 | [136-95-8] | GEO-00068 |
| Neu | 5-Amino-2-bromobenzoic acid | 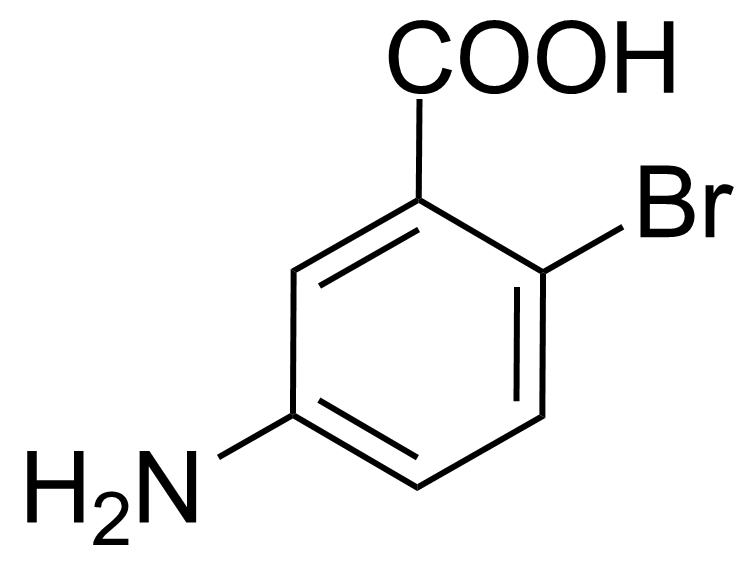 | [2840-02-0] | GEO-00082 |
| Neu | 2-Amino-6-bromobenzothiazole | 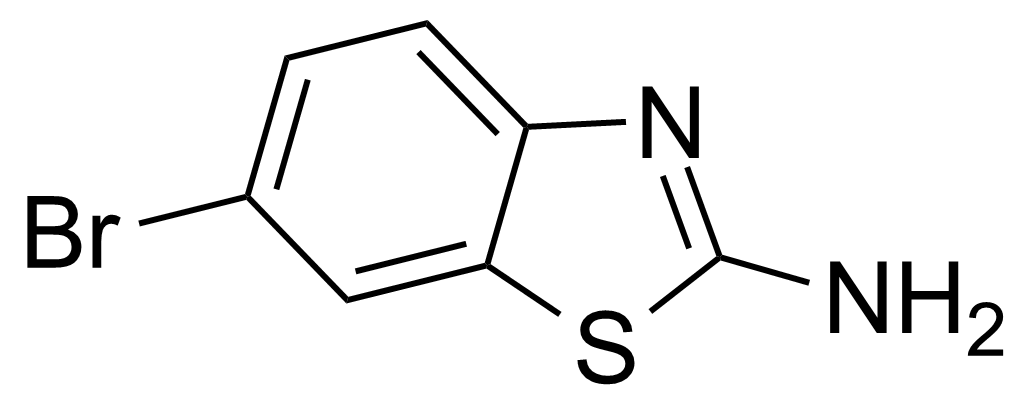 | [15864-32-1] | GEO-00083 |
| Neu | 6-Amino-5-bromo-1-methyluracil monohydrate | 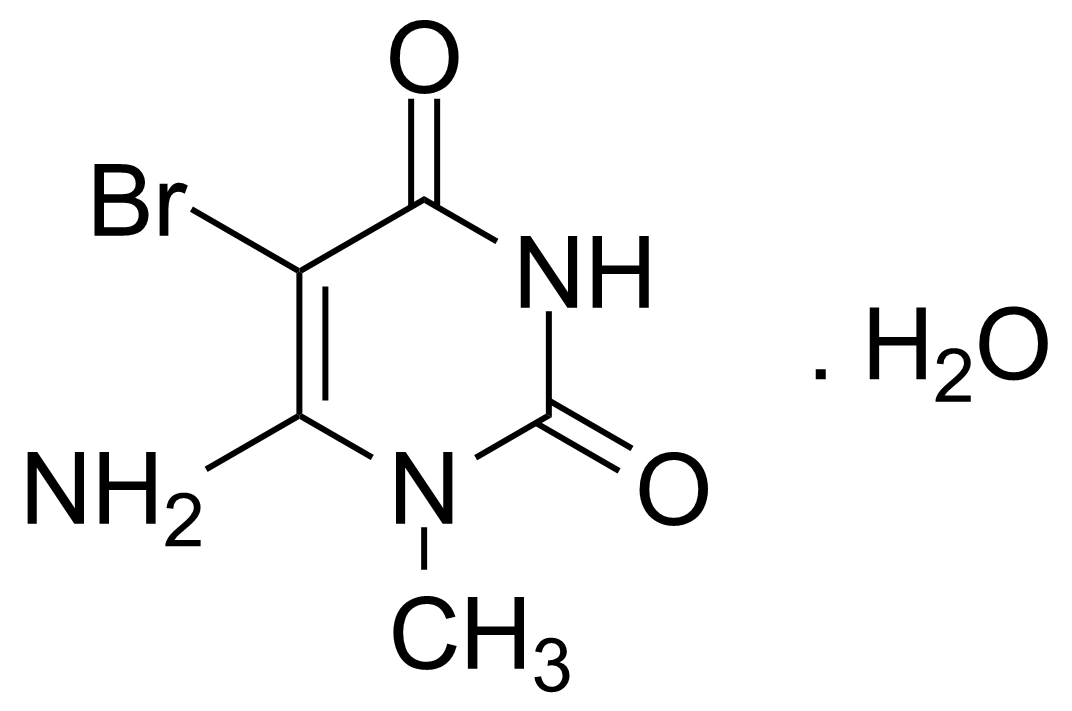 | [14094-37-2] | GEO-00087 |