 Januar 01, 1970
Januar 01, 1970Phenylpyruvic acid – preparation and application
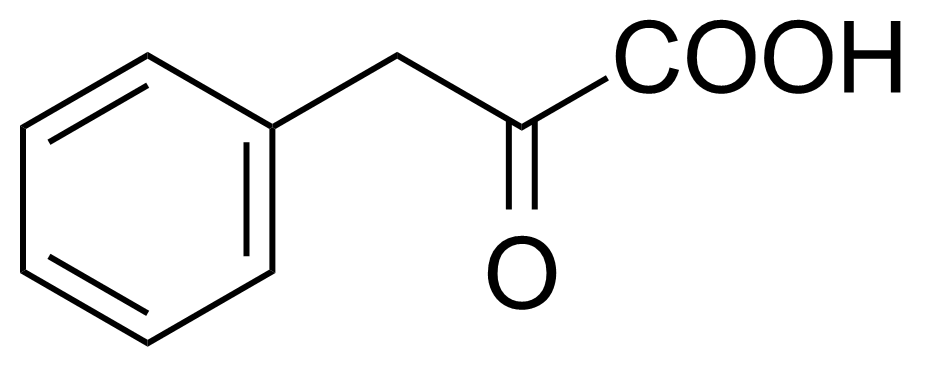
Phenylpyruvic acid [156-06-9] or 2-oxo-3-phenylpropanoic acid is a keto acid that exists in equilibrium with its E- and Z-enol tautomers. It is a white to yellow crystalline solid with the melting point of 150-154 °C.[1] It is a product from the oxidative deamination of phenylalanine. When the activity of the enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase is reduced, the amino acid phenylalanine accumulates and gets converted into phenylpyruvic acid (phenylpyruvate), which leads to Phenylketonuria.
Preparation of Phenylpyruvic acid:
It can pre prapared by hydrolysis of aminocinnamic acid derivatives e.g. α-acetaminocinnamic acid.[2] It has been prepared by condensation of benzaldehyde and glycine derivatives to give phenylazlactone, which is then hydrolyzed with acid- or base-catalysis.[3] It can also be synthesized by catalytic carbonylation of a benzyl halide in the presence of a catalytic system based on carbonyl complexes of cobalt or precursors.[4]
Application:
Phenylpyruvate derivatives can be potential inhibitors of the phenylpyruvate tautomerase activity catalysed by the Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Fator (MIF) which has been identified as a pro-inflammatory cytokine.[5] It was used in the synthesis of series of 7H-thiazolo[3,2-b]-1,2,4-triazin-7-one derivatives with anti-acetylcholinesterase activity.[6] Phenylpyruvate was used in the synthesis of quinoxaline derivatives targeting HIV reverse transcriptase enzyme.[7] Reductive amination of phenylpyruvic acid gives phenylalanine.[8]
Product categorization (Chemical groups):
Main category:
Second level:
Third level:
_______________________________________________________________________
[2] R. M. Herbst, D. Shemin Org. Synth. 1939, 19, 77. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.019.0077
[3] A. J. M. Carpy, P. P. Haasbroek, D. W. Oliver Med. Chem. Res. 2004, 13, 565. doi:10.1007/s00044-004-0102-y
[4] M. Foa, A. Moro, A. Gardano, L. Cassar Process for preparing phenyl pyruvic acids 1982, Montedison S.p.A. US4481369A.
[5] J. B. Lubetsky, M. Swope, C. Dealwis, P. Blake, E. Lolis Biochemistry 1999, 38 (22), 7346. doi:10.1021/bi990306m
[6] S. J. Liu, L. Yang, X. G. Liu, Y. Luo, Z. J. Cao, D. C. C. Wan, H. Q. Lin, C. Hu Lett. Drug Des. Discov. 2010, 7 (1), 5. doi:10.2174/157018010789869343
[7] L. Fabian, M. T. Porro, N. Gómez, M. Salvatori, G. Turk, D. Estrin, A. Moglioni Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 188, 111987. doi:10.1016/j.ejmech.2019.111987
[8] A. S. C. Chan, C. C. Chen, Y. C. Lin Appl. Catal. A: Gen 1994, 119 (1), L1. doi:10.1016/0926-860X(94)85018-6